Carotid chemoafferent activity is not necessary for all phrenic long-term facilitation following acute intermittent hypoxia
- PMID: 21093615
- PMCID: PMC4374991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2010.11.006
Carotid chemoafferent activity is not necessary for all phrenic long-term facilitation following acute intermittent hypoxia
Abstract
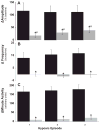
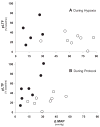
Phrenic long-term facilitation (pLTF) is a form of respiratory plasticity induced by acute intermittent hypoxia (AIH) or episodic carotid chemoafferent neuron activation. Surprisingly, residual pLTF is expressed in carotid denervated rats. However, since carotid denervation eliminates baroreceptor feedback and causes profound hypotension during hypoxia in anesthetized rats, potential contributions of these uncontrolled factors or residual chemoafferent neuron activity to residual pLTF cannot be ruled out. Since ATP is necessary for hypoxic carotid chemotransduction, we tested the hypothesis that functional peripheral chemoreceptor denervation (with intact baroreceptors) via systemic P2X receptor antagonism blocks hypoxic phrenic responses and AIH-induced pLTF in anesthetized rats. Pyridoxal-phosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulfonic acid (PPADS; 100 mg/kg i.v.), a non-selective P2X receptor antagonist, was administered to anesthetized, vagotomized, paralyzed and ventilated male Sprague-Dawley rats prior to AIH (3, 5 min episodes of 10% O(2); 5 min intervals). Although PPADS strongly attenuated the short-term hypoxic phrenic response (20 ± 4% vs. 113 ± 15% baseline; P < 0.001), pLTF was reduced but not eliminated 60 min post-AIH (25 ± 4% vs. 51 ± 11% baseline; n = 8 and 7, respectively; P < 0.002). Thus, AIH initiates residual pLTF out of proportion to the diminished hypoxic phrenic response and chemoafferent neuron activation. Although the mechanism of residual pLTF following functional chemo-denervation remains unclear, possible mechanisms involving direct effects of hypoxia on the CNS are discussed.
Copyright © 2011. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Aicher SA, Saravay RH, Cravo S, Jeske I, Morrison SF, Reis DJ, Milner TA. Monosynaptic projections from the nucleus tractus solitarii to C1 adrenergic neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla: comparison with input from the caudal ventrolateral medulla. J Comp Neurol. 1996;373 (1):62–75. - PubMed
-
- Bach KB, Mitchell GS. Hypoxia-induced long-term facilitation of respiratory activity is serotonin dependent. Respir Physiol. 1996;104:251–260. - PubMed
-
- Baker-Herman TL, Fuller DD, Bavis RW, Zabka AG, Golder FJ, Doperalski NJ, Johnson RA, Watters JJ, Mitchell GS. BDNF is necessary and sufficient for spinal respiratory plasticity following intermittent hypoxia. Nature Neuroscience. 2004;7:48–55. (Featured in News and Views, Nature Medicine 10:25–26) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

