Environmental noise affects auditory temporal processing development and NMDA-2B receptor expression in auditory cortex
- PMID: 21094188
- PMCID: PMC3022098
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2010.11.028
Environmental noise affects auditory temporal processing development and NMDA-2B receptor expression in auditory cortex
Abstract
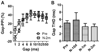
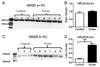
Auditory temporal processing is essential for sound discrimination and speech comprehension. Under normal developmental conditions, temporal processing acuity improves with age. As recent animal studies have shown that the functional development of the auditory cortex (AC) is impaired by early life exposure to environmental noise (i.e., continuous, moderate-level, white noise), here we investigated whether the normal age-related improvement in temporal processing acuity is sensitive to delayed development of the AC. We used a behavioral paradigm, the gap-induced prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex, to assess the gap detection threshold, and provide a comparison of temporal processing acuity between environmental noise-reared rats and age-matched controls. Moreover, because age-related changes normally occur in the relative expression of different N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunits, we assessed the level of protein expression of NMDA-2A and 2B receptors (NR2A and NR2B respectively) in the AC after environmental noise-rearing. As hypothesized, rats reared in environmental noise showed (1) poor temporal processing acuity as adults (i.e., gap detection threshold remained elevated at a juvenile-like level), and (2) an increased level of NR2B protein expression compared to age-matched controls. This poor temporal processing acuity represented delayed development rather than permanent impairment, as moving these environmental noise-reared rats to normal acoustic conditions improved their gap detection threshold to an age-appropriate level. Furthermore, housing normally reared, adult rats in environmental noise for two months did not affect their already-mature gap detection threshold. Thus, masking normal sound inputs with environmental noise during early life, but not adulthood, impairs temporal processing acuity as assessed with the gap detection threshold.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Environmental enrichment rescues the degraded auditory temporal resolution of cortical neurons induced by early noise exposure.Eur J Neurosci. 2015 Sep;42(5):2144-54. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12975. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Eur J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26059984
-
NR2B subunit-dependent long-term potentiation enhancement in the rat cortical auditory system in vivo following masking of patterned auditory input by white noise exposure during early postnatal life.Eur J Neurosci. 2009 Aug;30(3):376-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06835.x. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19656178
-
Neonatal nicotine exposure impairs development of auditory temporal processing.Hear Res. 2008 Nov;245(1-2):58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2008.08.009. Epub 2008 Sep 3. Hear Res. 2008. PMID: 18801421 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental acoustic enrichment promotes recovery from developmentally degraded auditory cortical processing.J Neurosci. 2014 Apr 16;34(16):5406-15. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5310-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24741032 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a modified prepulse inhibition paradigm to assess complex auditory discrimination in rodents.Brain Res Bull. 2008 May 15;76(1-2):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.07.013. Epub 2007 Aug 2. Brain Res Bull. 2008. PMID: 18395604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dependence of the Startle Response on Temporal and Spectral Characteristics of Acoustic Modulatory Influences in Rats and Gerbils.Front Behav Neurosci. 2016 Jun 30;10:133. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00133. eCollection 2016. Front Behav Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27445728 Free PMC article.
-
Low Intensity Noise Exposure Enhanced Auditory Loudness and Temporal Processing by Increasing Excitability of DCN.Neural Plast. 2022 Nov 21;2022:6463355. doi: 10.1155/2022/6463355. eCollection 2022. Neural Plast. 2022. PMID: 36452876 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Patterned Sound Deprivation on Short- and Long-Term Plasticity in the Rat Thalamocortical Auditory System In Vivo.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:3407135. doi: 10.1155/2016/3407135. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 26881106 Free PMC article.
-
Traffic noise disrupts vocal development and suppresses immune function.Sci Adv. 2021 May 12;7(20):eabe2405. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abe2405. Print 2021 May. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33980481 Free PMC article.
-
Parameter optimization for applying the prepulse gap paradigm to humans.Korean J Audiol. 2013 Dec;17(3):118-23. doi: 10.7874/kja.2013.17.3.118. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Korean J Audiol. 2013. PMID: 24653919 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

