Quantification of liver fat with magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 21094444
- PMCID: PMC3002753
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mric.2010.08.013
Quantification of liver fat with magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
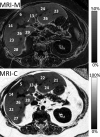
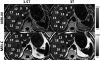
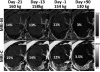
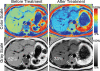
Intracellular fat accumulation is common feature of liver disease. Intracellular fat (steatosis) is the histologic hallmark of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease but also may occur with alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, HIV and genetic lipodystrophies, and chemotherapy. This article reviews emerging MR imaging techniques that attempt to quantify liver fat. The content provides an overview of fatty liver disease and diseases where fat is an important disease feature. Also discussed is the current use and limitation of nontargeted biopsy in diffuse liver disease and why quantitative noninvasive biomarkers of liver fat would be beneficial.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
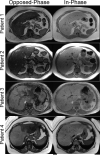
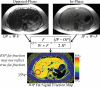
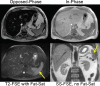

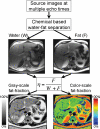

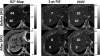
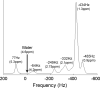
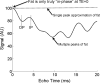
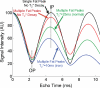


References
-
- Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J, et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2005 Jul;129(1):113–121. - PubMed
-
- Adams LA, Waters OR, Knuiman MW, Elliott RR, Olynyk JK. NAFLD as a risk factor for the development of diabetes and the metabolic syndrome: an eleven-year follow-up study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009 Apr;104(4):861–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

