Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) in retinal ischemic preconditioning
- PMID: 21094639
- PMCID: PMC3074007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2010.10.011
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) in retinal ischemic preconditioning
Abstract
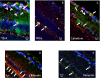
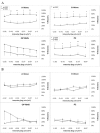
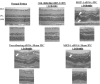
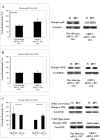
We previously described the phenomenon of retinal ischemic pre-conditioning (IPC) and we have shown the role of various signaling proteins in the protective pathways, including the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. In this study we examined the role in IPC of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1), which inactivates p38. Ischemia was produced by elevation of intraocular pressure above systolic arterial blood pressure in adult Wistar rats. Preconditioning was produced by transient retinal ischemia for 5 min, 24 h prior to ischemia. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) to MKP-1 or a control non-silencing siRNA, was injected into the vitreous 6 h prior to IPC. Recovery was assessed by electroretinography (ERG) and histology. The a-and b-waves, and oscillatory potentials (OPs), measured before and 1 week after ischemia, were then normalized relative to pre-ischemic baseline, and corrected for diurnal variation in the normal non-ischemic eye. The P2, or post-photoreceptor component of the ERG (which reflects function of the rod bipolar cells in the inner retina), was derived using the Hood-Birch model. MKP-1 was localized in specific retinal cells using immunohistochemistry; levels of mitogen-activated protein kinases were measured using Western blotting. Injection of siRNA to MKP-1 significantly attenuated the protective effect of IPC as reflected by decreased recovery of the electroretinogram a and b-waves and the P2 after ischemia. The injection of siRNA to MKP-1 reduced the number of cells in the retinal ganglion cell and outer nuclear layers after IPC and ischemia. Blockade of MKP-1 by siRNA also increased the activation of p38 at 24 h following IPC. MKP-1 siRNA did not alter the levels of phosphorylated jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) or extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) after IPC. The results suggest the involvement of dual-specificity phosphatase MKP-1 in IPC and that MKP-1 is involved in IPC by regulating levels of activated MAPK p38.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Boutros T, Chevet E, Metrakos P. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/MAP kinase phosphatase regulation: roles in cell growth, death, and cancer. Pharmacol Rev. 2008;60:261–310. - PubMed
-
- Brondello JM, Pouyssegur J, McKenzie FR. Reduced MAP kinase phosphatase-1 degradation after p42/p44MAPK-dependent phosphorylation. Science. 1999;286:2514–2517. - PubMed
-
- Bui BV, Edmunds B, Cioffi GA, Fortune B. The gradient of retinal functional changes during acute intraocular pressure elevation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46:202–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

