Redox regulation of the mitochondrial K(ATP) channel in cardioprotection
- PMID: 21094666
- PMCID: PMC3109179
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.11.005
Redox regulation of the mitochondrial K(ATP) channel in cardioprotection
Abstract
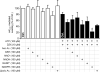
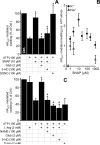
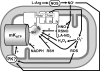
The mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channel (mK(ATP)) is important in the protective mechanism of ischemic preconditioning (IPC). The channel is reportedly sensitive to reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, and the aim of this study was to compare such species in parallel, to build a more comprehensive picture of mK(ATP) regulation. mK(ATP) activity was measured by both osmotic swelling and Tl(+) flux assays, in isolated rat heart mitochondria. An isolated adult rat cardiomyocyte model of ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury was also used to determine the role of mK(ATP) in cardioprotection by nitroxyl. Key findings were as follows: (i) mK(ATP) was activated by O(2)(-) and H(2)O(2) but not other peroxides. (ii) mK(ATP) was inhibited by NADPH. (iii) mK(ATP) was activated by S-nitrosothiols, nitroxyl, and nitrolinoleate. The latter two species also inhibited mitochondrial complex II. (iv) Nitroxyl protected cardiomyocytes against IR injury in an mK(ATP)-dependent manner. Overall, these results suggest that the mK(ATP) channel is activated by specific reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, and inhibited by NADPH. The redox modulation of mK(ATP) may be an underlying mechanism for its regulation in the context of IPC. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Mitochondria and Cardioprotection.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74:1124–1136. - PubMed
-
- Facundo HT, Fornazari M, Kowaltowski AJ. Tissue protection mediated by mitochondrial K+ channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1762:202–212. - PubMed
-
- Garlid KD, Dos SP, Xie ZJ, Costa AD, Paucek P. Mitochondrial potassium transport: the role of the mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K(+) channel in cardiac function and cardioprotection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2003;1606:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Murphy E, Steenbergen C. Preconditioning: the mitochondrial connection. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007;69:51–67. - PubMed
-
- Vanden Hoek TL, Becker LB, Shao Z, Li C, Schumacker PT. Reactive oxygen species released from mitochondria during brief hypoxia induce preconditioning in cardiomyocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:18092–18098. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

