Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin enhances liver damage in bile duct-ligated mice
- PMID: 21095216
- PMCID: PMC3011047
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2010.11.003
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin enhances liver damage in bile duct-ligated mice
Abstract
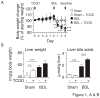
The environmental pollutant 2,3,7,8-tetracholorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is known to cause a wide variety of toxic effects, including hepatotoxicity, by way of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR). Although inducible expression of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A1 and CYP1A2 is associated with liver injury caused by high-dose TCDD, the specific role of the AHR-CYP1 cascade in hepatotoxicity remains unclear. We investigated the effects of AHR activation under conditions of cholestasis. We administered oral TCDD to mice at a dose that can effectively induce Cyp1 gene expression without overt liver toxicity and then ligated their bile ducts. TCDD pretreatment enhanced bile duct ligation (BDL)-induced increases in liver and plasma bile acids, bilirubin, and aminotransferases. Histology of TCDD-pretreated BDL mice revealed massive hepatic necrosis without any increase in number of apoptotic cells. Whereas induction of AHR-target genes by TCDD was observed similarly in sham-operated as well as in BDL mice, TCDD pretreatment of BDL mice altered the expression of hepatic genes involved in bile acid synthesis and transport. Increased plasma proinflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1β, in BDL mice were further elevated by TCDD pretreatment. Liver injury by TCDD plus BDL, such as increased plasma bile acids, bilirubin and aminotransferases, liver necrosis, and increased tumor necrosis factor production, was exaggerated in Cyp1a1/1a2(-/-) double knockout mice. These findings indicate that TCDD aggravates cholestatic liver damage and that the presence of CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 plays a protective role in liver damage caused by TCDD and BDL.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






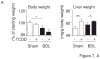
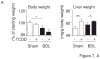
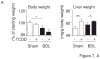
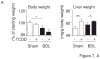
Similar articles
-
Deleterious effect of oltipraz on extrahepatic cholestasis in bile duct-ligated mice.J Hepatol. 2014 Jan;60(1):160-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.08.015. Epub 2013 Aug 23. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 23978715 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor results in distinct hepatic and renal phenotypes in rats and mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;272(2):503-18. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23859880
-
Altered thyroxin and retinoid metabolic response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in aryl hydrocarbon receptor-null mice.Arch Toxicol. 2005 May;79(5):260-7. doi: 10.1007/s00204-004-0626-4. Epub 2004 Nov 17. Arch Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15902423
-
Transgenic Overexpression of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Repressor (AhRR) and AhR-Mediated Induction of CYP1A1, Cytokines, and Acute Toxicity.Environ Health Perspect. 2016 Jul;124(7):1071-83. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1510194. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Environ Health Perspect. 2016. PMID: 26862745 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role of AhR in the expression of toxic effects by TCDD.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003 Feb 17;1619(3):263-8. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(02)00485-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003. PMID: 12573486 Review.
Cited by
-
Deleterious effect of oltipraz on extrahepatic cholestasis in bile duct-ligated mice.J Hepatol. 2014 Jan;60(1):160-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.08.015. Epub 2013 Aug 23. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 23978715 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling Prevents Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells and Liver Fibrogenesis in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2019 Sep;157(3):793-806.e14. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.05.066. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 31170413 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Discovery: Holistic Efficacy at the Special Organ Level of Pungent Flavored Compounds from Pungent Traditional Chinese Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 11;20(3):752. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030752. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30754631 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) mediated short-term effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on bile acid homeostasis in mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018 Mar 15;343:48-61. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.02.005. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29452137 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Organic Pollutants Modify Gut Microbiota-Host Metabolic Homeostasis in Mice Through Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation.Environ Health Perspect. 2015 Jul;123(7):679-88. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1409055. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Environ Health Perspect. 2015. PMID: 25768209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aitken AE, Richardson TA, Morgan ET. Regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters in inflammation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2006;46:123–149. - PubMed
-
- Bock KW, Kohle C. Ah receptor: Dioxin-mediated toxic responses as hints to deregulated physiologic functions. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72:393–404. - PubMed
-
- Boyer JL, Trauner M, Mennone A, Soroka CJ, Cai SY, Moustafa T, Zollner G, Lee JY, Ballatori N. Upregulation of a basolateral FXR-dependent bile acid efflux transporter OSTα-OSTβ in cholestasis in humans and rodents. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290:G1124–1130. - PubMed
-
- Diliberto JJ, Burgin D, Birnbaum LS. Role of CYP1A2 in hepatic sequestration of dioxin: studies using CYP1A2 knock-out mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;236:431–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

