Allele-selective inhibition of huntingtin expression by switching to an miRNA-like RNAi mechanism
- PMID: 21095568
- PMCID: PMC3021381
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.10.013
Allele-selective inhibition of huntingtin expression by switching to an miRNA-like RNAi mechanism
Abstract
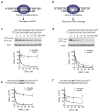
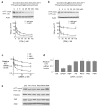
Inhibiting expression of huntingtin (HTT) protein is a promising strategy for treating Huntington's disease (HD), but indiscriminant inhibition of both wild-type and mutant alleles may lead to toxicity. An ideal silencing agent would block expression of mutant HTT while leaving expression of wild-type HTT intact. We observe that fully complementary duplex RNAs targeting the expanded CAG repeat within HTT mRNA block expression of both alleles. Switching the RNAi mechanism toward that used by miRNAs by introducing one or more mismatched bases into these duplex RNAs leads to potent (<10 nM) and highly selective (>30-fold relative to wild-type HTT) inhibition of mutant HTT expression in patient-derived cells. Potent, allele selective inhibition of HTT by mismatched RNAs provides a new option for developing HD therapeutics.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- De Souza EB, Cload ST, Pendergrast PS, Sah DW. Novel therapeutic modalities to address nondrugable protein interaction targets. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;34:142–158. - PubMed
-
- Drouet V, Perrin V, Hassig R, Dufour N, Auregan G, Alves S, Bonvento G, Brouillet E, Luthi-Carter R, Hantraye P, Deglon N. Sustained effects of nonallele-specific Huntingtin silencing. Ann Neurol. 2009;65:276–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

