Broad-spectrum antibiotic activity of the arylomycin natural products is masked by natural target mutations
- PMID: 21095572
- PMCID: PMC3003444
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.09.009
Broad-spectrum antibiotic activity of the arylomycin natural products is masked by natural target mutations
Abstract
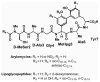
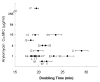
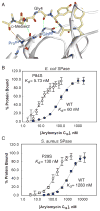
Novel classes of broad-spectrum antibiotics are needed to treat multidrug-resistant pathogens. The arylomycin class of natural products inhibits a promising antimicrobial target, type I signal peptidase (SPase), but upon initial characterization appeared to lack whole-cell activity against most pathogens. Here, we show that Staphylococcus epidermidis, which is sensitive to the arylomycins, evolves resistance via mutations in SPase and that analogous mutations are responsible for the natural resistance of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. We identify diverse bacteria lacking these mutations and demonstrate that most are sensitive to the arylomycins. The results illustrate that the arylomycins have a broad-spectrum of activity and are viable candidates for development into therapeutics. The results also raise the possibility that naturally occurring resistance may have masked other natural product scaffolds that might be developed into therapeutics.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Baltz RH. Marcel Faber Roundtable: is our antibiotic pipeline unproductive because of starvation, constipation or lack of inspiration? J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006;33:507–513. - PubMed
-
- Bumann D. Has nature already identified all useful antibacterial targets? Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008;11:387–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

