mTORC1 signaling under hypoxic conditions is controlled by ATM-dependent phosphorylation of HIF-1α
- PMID: 21095582
- PMCID: PMC3004768
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.10.030
mTORC1 signaling under hypoxic conditions is controlled by ATM-dependent phosphorylation of HIF-1α
Abstract
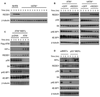
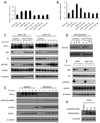
The mTOR complex-1 (mTORC1) coordinates cell growth and metabolism, acting as a restriction point under stress conditions such as low oxygen tension (hypoxia). Hypoxia suppresses mTORC1 signaling. However, the signals by which hypoxia suppresses mTORC1 are only partially understood, and a direct link between hypoxia-driven physiological stress and the regulation of mTORC1 signaling is unknown. Here we show that hypoxia results in ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM)-dependent phosphorylation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) on serine(696) and mediates downregulation of mTORC1 signaling. Deregulation of these pathways in pediatric solid tumor xenografts suggests a link between mTORC1 dysregulation and solid tumor development and points to an important role for hypoxic regulation of mTORC1 activity in tumor development.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are unaware of any actual or perceived conflict of interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
ATM: Promoter of metabolic "cost" reduction and "savings" usage during hypoxia through mTORC1 regulation.Mol Cell. 2010 Nov 24;40(4):501-2. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.11.013. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 21095578
References
-
- Arsham AM, Howell JJ, Simon MC. A novel hypoxia-inducible factor-independent hypoxic response regulating mammalian target of rapamycin and its targets. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:29655–29660. - PubMed
-
- Ateghang B, Wartenberg M, Gassmann M, Sauer H. Regulation of cardiotrophin-1 expression in mouse embryonic stem cells by HIF-1alpha and intracellular reactive oxygen species. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:1043–1052. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Horejsi Z, Koed K, Kramer A, Tort F, Zieger K, Guldberg P, Sehested M, Nesland JM, Lukas C, et al. DNA damage response as a candidate anti-cancer barrier in early human tumorigenesis. Nature. 2005;434:864–870. - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J, Rezaei N, Liontos M, Karakaidos P, Kletsas D, Issaeva N, Vassiliou LV, Kolettas E, Niforou K, Zoumpourlis VC, et al. Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature. 2006;444:633–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

