Characterization of lytic enzyme open reading frame 9 (ORF9) derived from Enterococcus faecalis bacteriophage phiEF24C
- PMID: 21097580
- PMCID: PMC3020548
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01540-10
Characterization of lytic enzyme open reading frame 9 (ORF9) derived from Enterococcus faecalis bacteriophage phiEF24C
Abstract
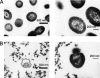
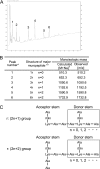
In bacteriophage (phage) therapy against Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Enterococcus faecalis, members of a genus of SPO1-like viruses are typically employed because of their extreme virulence and broad host spectrum. Phage φEF24C, which is a SPO1-like virus infecting E. faecalis, has previously been characterized as a therapeutic phage candidate. In addition to the phage itself, phage endolysin is also recognized as an effective antimicrobial agent. In this study, a putative endolysin gene (orf9) of E. faecalis phage φEF24C was analyzed in silico, and its activity was characterized using the recombinant form. First, bioinformatics analysis predicted that the open reading frame 9 (ORF9) protein is N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine amidase. Second, bacteriolytic and bactericidal activities of ORF9 against E. faecalis were confirmed by zymography, decrease of peptidoglycan turbidity, decrease of the viable count, and morphological analysis of ORF9-treated cells. Third, ORF9 did not appear to require Zn(2+) ions for its activity, contrary to the bioinformatics prediction of a Zn(2+) ion requirement. Fourth, the lytic spectrum was from 97.1% (34 out of 35 strains, including vancomycin-resistant strains) of E. faecalis strains to 60% (6 out of 10 strains) of Enterococcus faecium strains. Fifth, N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine amidase activity of ORF9 was confirmed by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) and the subsequent MALDI-postsource decay (PSD) analyses. Finally, functional analysis using N- or C-terminally deleted ORF9 mutants suggested that a complete ORF9 molecule is essential for its activity. These results suggested that ORF9 is an endolysin of phage φEF24C and can be a therapeutic alternative to antibiotics.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In silico and in vivo evaluation of bacteriophage phiEF24C, a candidate for treatment of Enterococcus faecalis infections.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Jul;74(13):4149-63. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02371-07. Epub 2008 May 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18456848 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriophage φEf11 ORF28 Endolysin, a Multifunctional Lytic Enzyme with Properties Distinct from All Other Identified Enterococcus faecalis Phage Endolysins.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Jun 17;85(13):e00555-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00555-19. Print 2019 Jul 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30979842 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of LysB4, an endolysin from the Bacillus cereus-infecting bacteriophage B4.BMC Microbiol. 2012 Mar 15;12:33. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-33. BMC Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22416675 Free PMC article.
-
Phage therapy: A renewed approach against oral diseases caused by Enterococcus faecalis infections.Microb Pathog. 2024 Apr;189:106574. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106574. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38354990 Review.
-
Recombinant bacteriophage lysins as antibacterials.Bioeng Bugs. 2010 Jan-Feb;1(1):9-16. doi: 10.4161/bbug.1.1.9818. Bioeng Bugs. 2010. PMID: 21327123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Phage Therapy in the Context of Enterococcus faecalis and Its Associated Diseases.Viruses. 2019 Apr 20;11(4):366. doi: 10.3390/v11040366. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31010053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endolysin LysEF-P10 shows potential as an alternative treatment strategy for multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecalis infections.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 31;7(1):10164. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10755-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28860505 Free PMC article.
-
Bactericidal synergism between phage endolysin Ply2660 and cathelicidin LL-37 against vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis biofilms.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2023 Apr 6;9(1):16. doi: 10.1038/s41522-023-00385-5. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2023. PMID: 37024490 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Two Novel Endolysins from Bacteriophage PEF1 and Evaluation of Their Combined Effects on the Control of Enterococcus faecalis Planktonic and Biofilm Cells.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Sep 13;13(9):884. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13090884. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335057 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteriolytic Potential of Enterococcus Phage iF6 Isolated from "Sextaphag®" Therapeutic Phage Cocktail and Properties of Its Endolysins, Gp82 and Gp84.Viruses. 2023 Mar 16;15(3):767. doi: 10.3390/v15030767. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carlton, R. M., W. H. Noordman, B. Biswas, E. D. de Meester, and M. J. Loessner. 2005. Bacteriophage P100 for control of Listeria monocytogenes in foods: genome sequence, bioinformatic analyses, oral toxicity study, and application. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 43:301-312. - PubMed
-
- Eliopoulos, G. M. 2009. Microbiology of drugs for treating multiply drug-resistant Gram-positive bacteria. J. Infect. 59(Suppl. 1):S17-S24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

