Differential responses of Bacillus subtilis rRNA promoters to nutritional stress
- PMID: 21097612
- PMCID: PMC3021234
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00708-10
Differential responses of Bacillus subtilis rRNA promoters to nutritional stress
Abstract
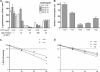
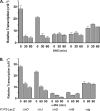
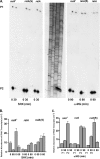
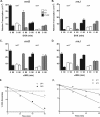
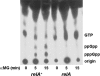
The in vivo expression levels of four rRNA promoter pairs (rrnp(1)p(2)) of Bacillus subtilis were determined by employing single-copy lacZ fusions integrated at the amyE locus. The rrnO, rrnJ, rrnD, and rrnB promoters displayed unique growth rate regulation and stringent responses. Both lacZ activity and mRNA levels were highest for rrnO under all growth conditions tested, while rrnJ, rrnB, and rrnD showed decreasing levels of activity. During amino acid starvation induced by serine hydroxamate (SHX), only the strong rrnO and rrnJ promoters demonstrated stringent responses. Under the growth conditions used, the rrn promoters showed responses similar to the responses to carbon source limitation induced by α-methyl glucoside (α-MG). The ratio of P2 to P1 transcripts, determined by primer extension analysis, was high for the strong rrnO and rrnJ promoters, while only P2 transcripts were detected for the weak rrnD and rrnB promoters. Cloned P1 or P2 promoter fragments of rrnO or rrnJ were differentially regulated. In wild-type (relA(+)) and suppressor [relA(S)] strains under the conditions tested, only P2 responded to carbon source limitation by a decrease in RNA synthesis, correlating with an increase in (p)ppGpp levels and a decrease in the GTP concentration. The weak P1 promoter elements remain relaxed in the three genetic backgrounds [relA(+), relA, relA(S)] in the presence of α-MG. During amino acid starvation, P2 was stringently regulated in relA(+) and relA(S) cells, while only rrnJp(1) was also regulated, but to a lesser extent. Both the relA(+) and relA(S) strains showed (p)ppGpp accumulation after α-MG treatment but not after SHX treatment. These data reveal the complex nature of B. subtilis rrn promoter regulation in response to stress, and they suggest that the P2 promoters may play a more prominent role in the stringent response.
Figures
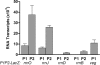
References
-
- Adyha, S., and M. Gottesman. 1982. Promoter occlusion: transcription through a promoter may inhibit its activity. Cell 29:939-944. - PubMed
-
- Afflerbach, H., O. Schroder, and R. Wagner. 1998. Effects of the Escherichia coli DNA-binding protein H-NS on rRNA synthesis in vivo. Mol. Microbiol. 28:641-653. - PubMed
-
- Anagnostopoulos, C., P. J. Piggot, and James A. Hoch. 1993. The genetic map of Bacillus subtilis, p. 425-462. In A. L. Sonenshein, J. A. Hoch, and R. Losick (ed.), Bacillus subtilis and its closest relatives: from genes to cells. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

