KaPPA-View4: a metabolic pathway database for representation and analysis of correlation networks of gene co-expression and metabolite co-accumulation and omics data
- PMID: 21097783
- PMCID: PMC3013809
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq989
KaPPA-View4: a metabolic pathway database for representation and analysis of correlation networks of gene co-expression and metabolite co-accumulation and omics data
Abstract
Correlations of gene-to-gene co-expression and metabolite-to-metabolite co-accumulation calculated from large amounts of transcriptome and metabolome data are useful for uncovering unknown functions of genes, functional diversities of gene family members and regulatory mechanisms of metabolic pathway flows. Many databases and tools are available to interpret quantitative transcriptome and metabolome data, but there are only limited ones that connect correlation data to biological knowledge and can be utilized to find biological significance of it. We report here a new metabolic pathway database, KaPPA-View4 (http://kpv.kazusa.or.jp/kpv4/), which is able to overlay gene-to-gene and/or metabolite-to-metabolite relationships as curves on a metabolic pathway map, or on a combination of up to four maps. This representation would help to discover, for example, novel functions of a transcription factor that regulates genes on a metabolic pathway. Pathway maps of the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and maps generated from their gene classifications are available at KaPPA-View4 KEGG version (http://kpv.kazusa.or.jp/kpv4-kegg/). At present, gene co-expression data from the databases ATTED-II, COXPRESdb, CoP and MiBASE for human, mouse, rat, Arabidopsis, rice, tomato and other plants are available.
Figures

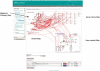

References
-
- Aoki K, Ogata Y, Shibata D. Approaches for extracting practical information from gene co-expression networks in plant biology. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007;48:381–390. - PubMed
-
- Usadel B, Obayashi T, Mutwil M, Giorgi FM, Bassel GW, Tanimoto M, Chow A, Steinhauser D, Persson S, Provart NJ. Co-expression tools for plant biology: opportunities for hypothesis generation and caveats. Plant Cell Environ. 2009;32:1633–1651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

