The MARCKS protein plays a critical role in phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate metabolism and directed cell movement in vascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 21097841
- PMCID: PMC3023526
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.196022
The MARCKS protein plays a critical role in phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate metabolism and directed cell movement in vascular endothelial cells
Abstract
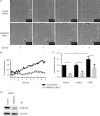
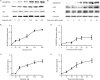
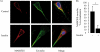
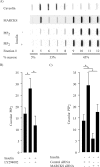
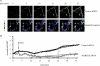
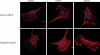
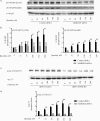
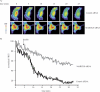
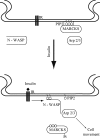
The MARCKS protein (myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate) is an actin- and calmodulin-binding protein that is expressed in many mammalian tissues. The role of MARCKS in endothelial signaling responses is incompletely understood. We found that siRNA-mediated knockdown of MARCKS in cultured endothelial cells abrogated directed cell movement in a wound healing assay. We used biochemical and cell imaging approaches to explore the role of MARCKS in endothelial signal transduction pathways activated by insulin. Insulin treatment of vascular endothelial cells promoted the dose- and time-dependent phosphorylation of MARCKS. Cell imaging and hydrodynamic approaches revealed that MARCKS is targeted to plasmalemmal caveolae and undergoes subcellular translocation in response to insulin. Insulin treatment promoted an increase in levels of the signaling phospholipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP(2)) in plasmalemmal caveolae. The insulin-stimulated increase in caveolar PIP(2) was blocked by siRNA-mediated knockdown of MARCKS, as determined using both biochemical assays and imaging studies using FRET-based PIP(2) biosensors. The critical role of PIP(2) in MARCKS responses was explored by examining the PIP(2)- and actin-binding proteins Arp2/3 and N-WASP. Insulin promoted the rapid and robust phosphorylation of both N-WASP and Arp2/3, but these phosphorylation responses were markedly attenuated by siRNA-mediated MARCKS knockdown. Moreover, MARCKS knockdown effectively abrogated N-WASP activation in response to insulin, as determined using a FRET-based N-WASP activity biosensor. Taken together, these studies show that MARCKS plays a key role in insulin-dependent endothelial signaling to PIP(2) and is a critical determinant of actin assembly and directed cell movement in the vascular endothelium.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

