Glucose and weight control in mice with a designed ghrelin O-acyltransferase inhibitor
- PMID: 21097901
- PMCID: PMC3068526
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1196154
Glucose and weight control in mice with a designed ghrelin O-acyltransferase inhibitor
Abstract
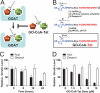
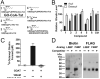
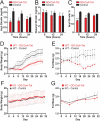
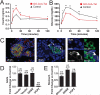
Ghrelin is a gastric peptide hormone that stimulates weight gain in vertebrates. The biological activities of ghrelin require octanoylation of the peptide on Ser(3), an unusual posttranslational modification that is catalyzed by the enzyme ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT). Here, we describe the design, synthesis, and characterization of GO-CoA-Tat, a peptide-based bisubstrate analog that antagonizes GOAT. GO-CoA-Tat potently inhibits GOAT in vitro, in cultured cells, and in mice. Intraperitoneal administration of GO-CoA-Tat improves glucose tolerance and reduces weight gain in wild-type mice but not in ghrelin-deficient mice, supporting the concept that its beneficial metabolic effects are due specifically to GOAT inhibition. In addition to serving as a research tool for mapping ghrelin actions, GO-CoA-Tat may help pave the way for clinical targeting of GOAT in metabolic diseases.
Figures
Comment in
-
Metabolic disease: GOAT inhibitors to battle the bulge?Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Jan;10(1):22. doi: 10.1038/nrd3345. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21193866 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

