Chymotrypsin C is a co-activator of human pancreatic procarboxypeptidases A1 and A2
- PMID: 21098023
- PMCID: PMC3023477
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.187369
Chymotrypsin C is a co-activator of human pancreatic procarboxypeptidases A1 and A2
Abstract
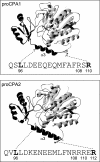
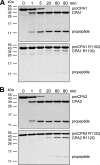
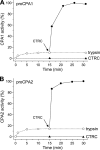
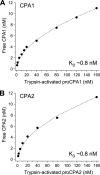
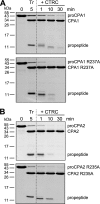
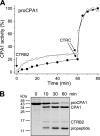
Human digestive carboxypeptidases CPA1, CPA2, and CPB1 are secreted by the pancreas as inactive proenzymes containing a 94-96-amino acid-long propeptide. Activation of procarboxypeptidases is initiated by proteolytic cleavage at the C-terminal end of the propeptide by trypsin. Here, we demonstrate that subsequent cleavage of the propeptide by chymotrypsin C (CTRC) induces a nearly 10-fold increase in the activity of trypsin-activated CPA1 and CPA2, whereas CPB1 activity is unaffected. Other human pancreatic proteases such as chymotrypsin B1, chymotrypsin B2, chymotrypsin-like enzyme-1, elastase 2A, elastase 3A, or elastase 3B are inactive or markedly less effective at promoting procarboxypeptidase activation. On the basis of these observations, we propose that CTRC is a physiological co-activator of proCPA1 and proCPA2. Furthermore, the results confirm and extend the notion that CTRC is a key regulator of digestive zymogen activation.
Figures


References
-
- Folk J. E., Schirmer E. W. (1965) J. Biol. Chem. 240, 181–192 - PubMed
-
- Folk J. E., Cole P. W. (1965) J. Biol. Chem. 240, 193–197 - PubMed
-
- Keil-Dlouha V., Puigserver A., Marie A., Keil B. (1972) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 276, 531–535 - PubMed
-
- Iio-Akama K., Sasamoto H., Miyazawa K., Miura S., Tobita T. (1985) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 831, 249–256 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

