A rapid, high-throughput viability assay for Blastocystis spp. reveals metronidazole resistance and extensive subtype-dependent variations in drug susceptibilities
- PMID: 21098237
- PMCID: PMC3028762
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00900-10
A rapid, high-throughput viability assay for Blastocystis spp. reveals metronidazole resistance and extensive subtype-dependent variations in drug susceptibilities
Abstract
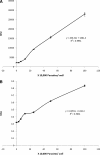
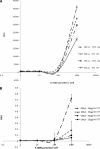
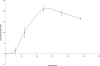
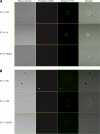
Blastocystis is an emerging protistan parasite of controversial pathogenesis. Although metronidazole (Mz) is standard therapy for Blastocystis infections, there have been accumulating reports of treatment failure, suggesting the existence of drug-resistant isolates. Furthermore, very little is known about Blastocystis susceptibility to standard antimicrobials. In the present study, we established resazurin and XTT viability microassays for Blastocystis spp. belonging to subtypes 4 and 7, both of which have been suggested to represent pathogenic zoonotic subtypes. The optimized resazurin assay was used to screen a total of 19 compounds against both subtypes. Interestingly, subtype 7 parasites were resistant to Mz, a 1-position-substituted 5-nitroimidazole (5-NI), while subtype 4 parasites were sensitive. Some cross-resistance was observed to tinidazole, another 1-position 5-NI. Conversely, subtype 4 parasites were resistant to emetine, while subtype 7 parasites were sensitive. Position 2 5-NIs were effective against both subtypes, as were ornidazole, nitazoxanide, furazolidone, mefloquine, quinicrine, quinine, cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole), and iodoacetamide. Both subtypes were resistant to chloroquine, doxycycline, paromomycin, ampicillin, and pyrimethamine. This is the first study to report extensive variations in drug sensitivities among two clinically important subtypes. Our study highlights the need to reevaluate established treatment regimens for Blastocystis infections and offers clear new treatment options for Mz treatment failures.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In Vitro Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns of Blastocystis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Aug;59(8):4417-23. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04832-14. Epub 2015 May 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25987633 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis in Blastocystis spp. is related to subtype.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2012 Dec;106(12):725-30. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2012.08.005. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2012. PMID: 23141370
-
Development of metronidazole-resistant lines of Blastocystis sp.Parasitol Res. 2012 Jul;111(1):441-50. doi: 10.1007/s00436-012-2860-7. Epub 2012 Feb 24. Parasitol Res. 2012. PMID: 22362365
-
Eradication of Blastocystis carriage with antimicrobials: reality or delusion?J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010 Feb;44(2):85-90. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181bb86ba. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 19834337 Review.
-
Eradication of Blastocystis in humans: Really necessary for all?Parasitol Int. 2016 Dec;65(6 Pt B):797-801. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2016.01.010. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Parasitol Int. 2016. PMID: 26780545 Review.
Cited by
-
Blastocystis: Consensus of treatment and controversies.Trop Parasitol. 2013 Jan;3(1):35-9. doi: 10.4103/2229-5070.113901. Trop Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23961439 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory function of Blastocystis spp. on the immune inflammatory response in the gut microbiome.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Aug 31;12:967724. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.967724. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36118018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Blastocystis Activity In Vitro of Egyptian Herbal Extracts (Family: Asteraceae) with Emphasis on Artemisia judaica.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 May 3;16(9):1555. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16091555. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31058875 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-subtype variation in enteroadhesion accounts for differences in epithelial barrier disruption and is associated with metronidazole resistance in Blastocystis subtype-7.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 May 22;8(5):e2885. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002885. eCollection 2014 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 24851944 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding drug resistance in human intestinal protozoa.Parasitol Res. 2015 May;114(5):1647-59. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4423-1. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Parasitol Res. 2015. PMID: 25782683 Review.
References
-
- Adagu, I. S., D. Nolder, D. C. Warhurst, and J. F. Rossignol. 2002. In vitro activity of nitazoxanide and related compounds against isolates of Giardia intestinalis, Entamoeba histolytica and Trichomonas vaginalis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 49:103-111. - PubMed
-
- Armentia, A., et al. 1993. Urticaria by Blastocystis hominis. Successful treatment with paromomycin. Allergol. Immunopathol. 21:149-151. - PubMed
-
- Bassily, S., Z. Farid, N. A. el-Masry, and E. M. Mikhail. 1987. Treatment of intestinal E. histolytica and G. lamblia with metronidazole, tinidazole and ornidazole: a comparative study. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 90:9-12. - PubMed
-
- Bénéré, E., R. A. da Luz, M. Vermeersch, P. Cos, and L. Maes. 2007. A new quantitative in vitro microculture method for Giardia duodenalis trophozoites. J. Microbiol. Methods 71:101-106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

