Alzheimer's disease peptide beta-amyloid interacts with fibrinogen and induces its oligomerization
- PMID: 21098282
- PMCID: PMC3003082
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1010373107
Alzheimer's disease peptide beta-amyloid interacts with fibrinogen and induces its oligomerization
Abstract
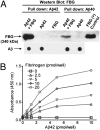
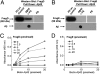
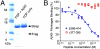
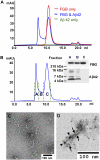
Increasing evidence supports a vascular contribution to Alzheimer's disease (AD), but a direct connection between AD and the circulatory system has not been established. Previous work has shown that blood clots formed in the presence of the β-amyloid peptide (Aβ), which has been implicated in AD, have an abnormal structure and are resistant to degradation in vitro and in vivo. In the present study, we show that Aβ specifically interacts with fibrinogen with a K(d) of 26.3 ± 6.7 nM, that the binding site is located near the C terminus of the fibrinogen β-chain, and that the binding causes fibrinogen to oligomerize. These results suggest that the interaction between Aβ and fibrinogen modifies fibrinogen's structure, which may then lead to abnormal fibrin clot formation. Overall, our study indicates that the interaction between Aβ and fibrinogen may be an important contributor to the vascular abnormalities found in AD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
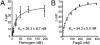
References
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Cleary JP, et al. Natural oligomers of the amyloid-beta protein specifically disrupt cognitive function. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Glenner GG, Wong CW. Alzheimer's disease: Initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984;120:885–890. - PubMed
-
- Roth M, Tomlinson BE, Blessed G. Correlation between scores for dementia and counts of ‘senile plaques’ in cerebral grey matter of elderly subjects. Nature. 1966;209:109–110. - PubMed
-
- Thal DR, Griffin WS, de Vos RA, Ghebremedhin E. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy and its relationship to Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2008;115:599–609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

