RNA polymerase 1-driven transcription as a mediator of BDNF-induced neurite outgrowth
- PMID: 21098478
- PMCID: PMC3039349
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.170134
RNA polymerase 1-driven transcription as a mediator of BDNF-induced neurite outgrowth
Abstract
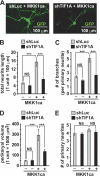
Neurite outgrowth is essential for development of the nervous system. Neurotrophins including BDNF are among extracellular signals that regulate neurite outgrowth. The ERK1/2 pathway contributes to intracellular signaling networks transducing the pro-neuritic effects of BDNF. In the nucleolus, RNA polymerase-1 (Pol1)-mediated transcription regulates ribosomal biogenesis, enabling cellular protein synthesis and growth. Hence, we tested the possibility that Pol1 is an effector for pro-neuritic signals such as BDNF. We report that Pol1-mediated nucleolar transcription was increased by BDNF in an ERK1/2-dependent manner in rat forebrain neurons. Conversely, in cultured hippocampal neurons, knockdown of a Pol1 coactivator, transcription initiation factor 1A (TIF1A), attenuated BDNF- or ERK1/2-induced neurite outgrowth. Also, upon overexpression, a constitutively active mutant of TIF1A strongly promoted neurite outgrowth, including increases in total neurite length and branching. Finally, overexpression of wild-type TIF1A enhanced the pro-neuritic effects of ERK1/2 activation. These observations indicate that the Pol1-mediated nucleolar transcription regulates neurite outgrowth and serves as a major pro-neuritic effector of the BDNF-activated ERK1/2 pathway. Thus, development of the nervous system appears critically dependent on the nucleolus.
Figures





References
-
- Parrish J. Z., Emoto K., Kim M. D., Jan Y. N. (2007) Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 30, 399–423 - PubMed
-
- Miller F. D., Kaplan D. R. (2003) Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 13, 391–398 - PubMed
-
- Dijkhuizen P. A., Ghosh A. (2005) Prog. Brain Res. 147, 17–27 - PubMed
-
- Redmond L., Kashani A. H., Ghosh A. (2002) Neuron 34, 999–1010 - PubMed
-
- Wayman G. A., Impey S., Marks D., Saneyoshi T., Grant W. F., Derkach V., Soderling T. R. (2006) Neuron 50, 897–909 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

