The Rho kinase Rock2b establishes anteroposterior asymmetry of the ciliated Kupffer's vesicle in zebrafish
- PMID: 21098560
- PMCID: PMC2998165
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.052985
The Rho kinase Rock2b establishes anteroposterior asymmetry of the ciliated Kupffer's vesicle in zebrafish
Abstract
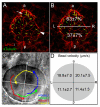
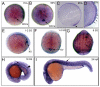
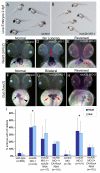
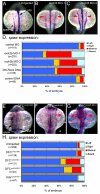
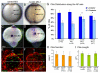
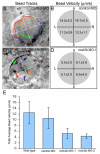
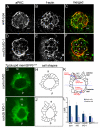
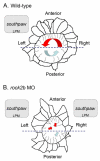
The vertebrate body plan features a consistent left-right (LR) asymmetry of internal organs. In several vertebrate embryos, motile cilia generate an asymmetric fluid flow that is necessary for normal LR development. However, the mechanisms involved in orienting LR asymmetric flow with previously established anteroposterior (AP) and dorsoventral (DV) axes remain poorly understood. In zebrafish, asymmetric flow is generated in Kupffer's vesicle (KV). The cellular architecture of KV is asymmetric along the AP axis, with more ciliated cells densely packed into the anterior region. Here, we identify a Rho kinase gene, rock2b, which is required for normal AP patterning of KV and subsequent LR development in the embryo. Antisense depletion of rock2b in the whole embryo or specifically in the KV cell lineage perturbed asymmetric gene expression in lateral plate mesoderm and disrupted organ LR asymmetries. Analyses of KV architecture demonstrated that rock2b knockdown altered the AP placement of ciliated cells without affecting cilia number or length. In control embryos, leftward flow across the anterior pole of KV was stronger than rightward flow at the posterior end, correlating with the normal AP asymmetric distribution of ciliated cells. By contrast, rock2b knockdown embryos with AP patterning defects in KV exhibited randomized flow direction and equal flow velocities in the anterior and posterior regions. Live imaging of Tg(dusp6:memGFP)(pt19) transgenic embryos that express GFP in KV cells revealed that rock2b regulates KV cell morphology. Our results suggest a link between AP patterning of the ciliated Kupffer's vesicle and LR patterning of the zebrafish embryo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regional cell shape changes control form and function of Kupffer's vesicle in the zebrafish embryo.Dev Biol. 2012 Oct 1;370(1):52-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.07.019. Epub 2012 Jul 26. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22841644 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of gene function and visualization of cilia-generated fluid flow in Kupffer's vesicle.J Vis Exp. 2013 Mar 31;(73):50038. doi: 10.3791/50038. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 23567922 Free PMC article.
-
Kupffer's vesicle is a ciliated organ of asymmetry in the zebrafish embryo that initiates left-right development of the brain, heart and gut.Development. 2005 Mar;132(6):1247-60. doi: 10.1242/dev.01663. Epub 2005 Feb 16. Development. 2005. PMID: 15716348
-
Salient features of the ciliated organ of asymmetry.Bioarchitecture. 2014 Jan-Feb;4(1):6-15. doi: 10.4161/bioa.28014. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Bioarchitecture. 2014. PMID: 24481178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Left-right asymmetry in zebrafish.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Sep;69(18):3069-77. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0985-6. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22527718 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regional cell shape changes control form and function of Kupffer's vesicle in the zebrafish embryo.Dev Biol. 2012 Oct 1;370(1):52-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.07.019. Epub 2012 Jul 26. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22841644 Free PMC article.
-
Natural reversal of cavefish heart asymmetry is controlled by Sonic Hedgehog effects on the left-right organizer.Development. 2024 Jul 15;151(14):dev202611. doi: 10.1242/dev.202611. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Development. 2024. PMID: 38940473 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide analysis reveals Zic3 interaction with distal regulatory elements of stage specific developmental genes in zebrafish.PLoS Genet. 2013 Oct;9(10):e1003852. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003852. Epub 2013 Oct 31. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24204288 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential action of JNK genes establishes the embryonic left-right axis.Development. 2022 May 1;149(9):dev200136. doi: 10.1242/dev.200136. Epub 2022 May 3. Development. 2022. PMID: 35352808 Free PMC article.
-
Pkd2 Affects Cilia Length and Impacts LR Flow Dynamics and Dand5.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 1;9:624531. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.624531. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amack J. D., Yost H. J. (2004). The T box transcription factor no tail in ciliated cells controls zebrafish left-right asymmetry. Curr. Biol. 14, 685-690 - PubMed
-
- Amack J. D., Wang X., Yost H. J. (2007). Two T-box genes play independent and cooperative roles to regulate morphogenesis of ciliated Kupffer's vesicle in zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 310, 196-210 - PubMed
-
- Borovina A., Superina S., Voskas D., Ciruna B. (2010). Vangl2 directs the posterior tilting and asymmetric localization of motile primary cilia. Nat. Cell. Biol. 12, 407-412 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

