The putative lipid transporter, Arv1, is required for activating pheromone-induced MAP kinase signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 21098723
- PMCID: PMC3030489
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.120725
The putative lipid transporter, Arv1, is required for activating pheromone-induced MAP kinase signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
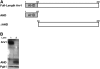
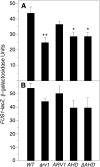
Saccharomyces cerevisiae haploid cells respond to extrinsic mating signals by forming polarized projections (shmoos), which are necessary for conjugation. We have examined the role of the putative lipid transporter, Arv1, in yeast mating, particularly the conserved Arv1 homology domain (AHD) within Arv1 and its role in this process. Previously it was shown that arv1 cells harbor defects in sphingolipid and glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) biosyntheses and may harbor sterol trafficking defects. Here we demonstrate that arv1 cells are mating defective and cannot form shmoos. They lack the ability to initiate pheromone-induced G1 cell cycle arrest, due to failure to polarize PI(4,5)P(2) and the Ste5 scaffold, which results in weakened MAP kinase signaling activity. A mutant Ste5, Ste5(Q59L), which binds more tightly to the plasma membrane, suppresses the MAP kinase signaling defects of arv1 cells. Filipin staining shows arv1 cells contain altered levels of various sterol microdomains that persist throughout the mating process. Data suggest that the sterol trafficking defects of arv1 affect PI(4,5)P(2) polarization, which causes a mislocalization of Ste5, resulting in defective MAP kinase signaling and the inability to mate. Importantly, our studies show that the AHD of Arv1 is required for mating, pheromone-induced G1 cell cycle arrest, and for sterol trafficking.
Figures







References
-
- Bagnat, M., and K. Simons, 2002. b Lipid rafts in protein sorting and cell polarity in budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biol. Chem. 383 1475–1480. - PubMed
-
- Beh, C. T., and J. Rine, 2004. A role for yeast oxysterol-binding protein homologs in endocytosis and in the maintenance of intracellular sterol-lipid distribution. J. Cell Sci. 117 2983–2996. - PubMed
-
- Berlin, V., J. Brill, J. Trueheart, J. D. Boeke and G. R. Fink, 1991. Genetic screens and selections for cell and nuclear fusion mutants. Methods Enzymol. 194 774–792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

