The role of the Arabidopsis morning loop components CCA1, LHY, PRR7, and PRR9 in temperature compensation
- PMID: 21098730
- PMCID: PMC3015110
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.110.079087
The role of the Arabidopsis morning loop components CCA1, LHY, PRR7, and PRR9 in temperature compensation
Abstract
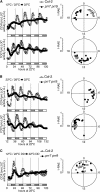
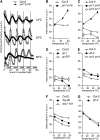
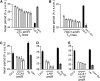
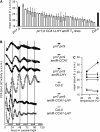
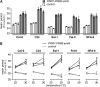
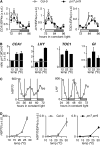
A defining, yet poorly understood characteristic of the circadian clock is that it is buffered against changes in temperature such that the period length is relatively constant across a range of physiologically relevant temperatures. We describe here the role of PSEUDO RESPONSE REGULATOR7 (PRR7) and PRR9 in temperature compensation. The Arabidopsis thaliana circadian oscillator comprises a series of interlocking feedback loops, and PRR7 and PRR9 function in the morning loop. The prr7 prr9 double mutant displays a unique phenotype that has not been observed before in other Arabidopsis clock mutants. In the prr7 prr9 mutant, the effects of temperature are overcompensated, apparently due to hyperactivation of the transcription factors CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED1 (CCA1) and LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL (LHY). Inactivation of CCA1 and LHY fully suppresses the overcompensation defects of prr7 prr9 mutants and rescues their long period phenotype. Overcompensation in prr7 prr9 mutants does not rely on FLOWERING LOCUS C, a previously identified gene required for temperature compensation. Together, our results reveal a role of PRR7 and PRR9 in regulating CCA1 and LHY activities in response to ambient temperature.
Figures
Comment in
-
Temperature compensation of the circadian clock: a role for the morning loop.Plant Cell. 2010 Nov;22(11):3506. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.221111. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 21098732 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

