Glucose-dependent potentiation of mouse islet insulin secretion by Epac activator 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP-AM
- PMID: 21099281
- PMCID: PMC2859731
- DOI: 10.4161/isl.1.3.9645
Glucose-dependent potentiation of mouse islet insulin secretion by Epac activator 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP-AM
Abstract
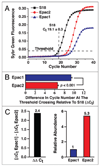
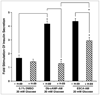
Epac2 is a cAMP-regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factor (cAMP-GEF) that is proposed to mediate stimulatory actions of the second messenger cAMP on mouse islet insulin secretion. Here we have used methods of islet perifusion to demonstrate that the acetoxymethyl ester (AM-ester) of an Epac-selective cAMP analog (ESCA) penetrates into mouse islets and is capable of potentiating both first and second phases of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). When used at low concentrations (1-10 μM), 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP-AM activates Rap1 GTPase but exhibits little or no ability to activate protein kinase A (PKA), as validated in assays of in vitro PKA activity (phosphorylation of Kemptide), Ser (133) CREB phosphorylation status, RIP1-CRE-Luc reporter gene activity, and PKA-dependent AKAR3 biosensor activation. Since quantitative PCR demonstrates Epac2 mRNA to be expressed at levels ca. 5.3-fold greater than that of Epac1, available evidence indicates that Epac2 does in fact mediate stimulatory actions of cAMP on mouse islet GSIS.
Figures


References
-
- Drucker DJ. Glucagon-like peptides. Diabetes. 1998;47:159–169. - PubMed
-
- Kieffer TJ, Habener JF. Glucagon-like peptides. Endocrine Reviews. 1999;20:876–913. - PubMed
-
- Holst JJ. Glucagon-like peptide-1: a gastrointestinal hormone with a pharmaceutical potential. Current Med Chem. 1999;6:1005–1017. - PubMed
-
- Nauck MA. Unraveling the science of incretin biology. Am J Med. 2009;122:3–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
