Signaling diversity of PKA achieved via a Ca2+-cAMP-PKA oscillatory circuit
- PMID: 21102470
- PMCID: PMC3073414
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.478
Signaling diversity of PKA achieved via a Ca2+-cAMP-PKA oscillatory circuit
Abstract
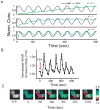
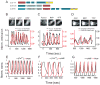
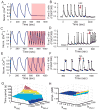
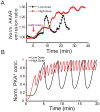
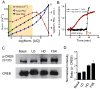
Many protein kinases are key nodal signaling molecules that regulate a wide range of cellular functions. These functions may require complex spatiotemporal regulation of kinase activities. Here, we show that protein kinase A (PKA), Ca(2+) and cyclic AMP (cAMP) oscillate in sync in insulin-secreting MIN6 beta cells, forming a highly integrated oscillatory circuit. We found that PKA activity was essential for this oscillatory circuit and was capable of not only initiating the signaling oscillations but also modulating their frequency, thereby diversifying the spatiotemporal control of downstream signaling. Our findings suggest that exquisite temporal control of kinase activity, mediated via signaling circuits resulting from cross-regulation of signaling pathways, can encode diverse inputs into temporal parameters such as oscillation frequency, which in turn contribute to proper regulation of complex cellular functions in a context-dependent manner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science. 2002;298:1912–1934. - PubMed
-
- Ubersax JA, Ferrell JE., Jr Mechanisms of specificity in protein phosphorylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:530–541. - PubMed
-
- Marshall CJ. Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell. 1995;80:179–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

