A large homozygous deletion in the SAMHD1 gene causes atypical Aicardi-Goutiéres syndrome associated with mtDNA deletions
- PMID: 21102625
- PMCID: PMC3062001
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2010.213
A large homozygous deletion in the SAMHD1 gene causes atypical Aicardi-Goutiéres syndrome associated with mtDNA deletions
Abstract
Aicardi-Goutiéres syndrome (AGS) is a genetic neurodegenerative disorder with clinical symptoms mimicking a congenital viral infection. Five causative genes have been described: three prime repair exonuclease1 (TREX1), ribonucleases H2A, B and C, and most recently SAM domain and HD domain 1 (SAMHD1). We performed a detailed clinical and molecular characterization of a family with autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder showing white matter destruction and calcifications, presenting in utero and associated with multiple mtDNA deletions. A muscle biopsy was normal and did not show any evidence of respiratory chain dysfunction. Southern blot analysis of tissue from a living child and affected fetuses demonstrated multiple mtDNA deletions. Molecular analysis of genes involved in mtDNA synthesis and maintenance (POLGα, POLGβ, Twinkle, ANT1, TK2, SUCLA1 and DGOUK) revealed normal sequences. Sequencing of TREX1 and ribonucleases H2A, B and C failed to reveal any mutations. Whole-genome homozygosity mapping revealed a candidate region containing the SAMHD1 gene. Sequencing of the gene in the affected child and two affected fetuses revealed a large deletion (9 kb), spanning the promoter, exon1 and intron 1. The parents were found to be heterozygous for this deletion. The identification of a homozygous large deletion in the SAMHD1 gene causing atypical AGS with multiple mtDNA deletions may add information regarding the involvement of mitochondria in self-activation of innate immunity by cell intrinsic components.
© 2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 1018-4813/11
Figures
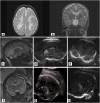
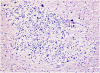
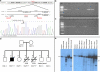
References
-
- Orcesi S, La Piana R, Fazzi E. Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome. Br Med Bull. 2009;89:183–201. - PubMed
-
- Crow YJ, Livingston JH. Aicardi-Goutières syndrome: an important Mendelian mimic of congenital infection. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2008;50:410–416. - PubMed
-
- Dale RC, Gornall H, Singh-Grewal D, Alcausin M, Rice GI, Crow YJ. Familial Aicardi-Goutières syndrome due to SAMHD1 mutations is associated with chronic arthropathy and contractures. Am J Med Genet A. 2010;152A:938–942. - PubMed
-
- Prasad AN, Malinger G, Lerman-Sagie T. Primary disorders of metabolism and disturbed fetal brain development. Clin Perinatol. 2009;36:621–638. - PubMed
-
- Dinopoulos A, Cecil KM, Schapiro MB, et al. Brain MRI and proton MRS findings in infants and children with respiratory chain defects. Neuropediatrics. 2005;36:290–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

