Sox2 is essential for formation of trophectoderm in the preimplantation embryo
- PMID: 21103067
- PMCID: PMC2980489
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013952
Sox2 is essential for formation of trophectoderm in the preimplantation embryo
Abstract
Background: In preimplantation mammalian development the transcription factor Sox2 (SRY-related HMG-box gene 2) forms a complex with Oct4 and functions in maintenance of self-renewal of the pluripotent inner cell mass (ICM). Previously it was shown that Sox2-/- embryos die soon after implantation. However, maternal Sox2 transcripts may mask an earlier phenotype. We investigated whether Sox2 is involved in controlling cell fate decisions at an earlier stage.
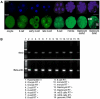
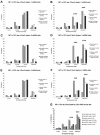
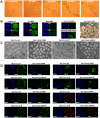
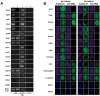
Methods and findings: We addressed the question of an earlier role for Sox2 using RNAi, which removes both maternal and embryonic Sox2 mRNA present during the preimplantation period. By depleting both maternal and embryonic Sox2 mRNA at the 2-cell stage and monitoring embryo development in vitro we show that, in the absence of Sox2, embryos arrest at the morula stage and fail to form trophectoderm (TE) or cavitate. Following knock-down of Sox2 via three different short interfering RNA (siRNA) constructs in 2-cell stage mouse embryos, we have shown that the majority of embryos (76%) arrest at the morula stage or slightly earlier and only 18.7-21% form blastocysts compared to 76.2-83% in control groups. In Sox2 siRNA-treated embryos expression of pluripotency associated markers Oct4 and Nanog remained unaffected, whereas TE associated markers Tead4, Yap, Cdx2, Eomes, Fgfr2, as well as Fgf4, were downregulated in the absence of Sox2. Apoptosis was also increased in Sox2 knock-down embryos. Rescue experiments using cell-permeant Sox2 protein resulted in increased blastocyst formation from 18.7% to 62.6% and restoration of Sox2, Oct4, Cdx2 and Yap protein levels in the rescued Sox2-siRNA blastocysts.
Conclusion and significance: We conclude that the first essential function of Sox2 in the preimplantation mouse embryo is to facilitate establishment of the trophectoderm lineage. Our findings provide a novel insight into the first differentiation event within the preimplantation embryo, namely the segregation of the ICM and TE lineages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
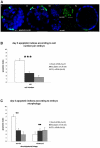
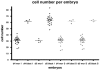
References
-
- Pevny LH, Lovell-Badge R. Sox genes find their feet. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1997;7:338–344. - PubMed
-
- Scaffidi P, Bianchi ME. Spatially precise DNA bending is an essential activity of the Sox-2 transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:47296–47301. - PubMed
-
- Wiebe MS, Wilder PJ, Kelly D, Rizzino A. Isolation, characterization, and differential expression of the murine Sox-2 promoter. Gene. 2000;246:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Collignon J, Sockanathan S, Hacker A, Cohen–Tannoudji M, Norris D, et al. A comparison of the properties of Sox-3 with SRY and two related genes, Sox-1 and Sox-2. Development. 1996;122:509–520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

