Liver steatosis and increased ChREBP expression in mice carrying a liver specific SIRT1 null mutation under a normal feeding condition
- PMID: 21103071
- PMCID: PMC2990071
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.6.682
Liver steatosis and increased ChREBP expression in mice carrying a liver specific SIRT1 null mutation under a normal feeding condition
Abstract
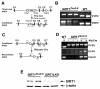
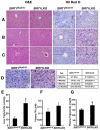
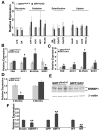
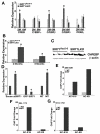
SIRT1, a homolog of yeast Sir2, is a type III NAD(+) dependent histone and protein deacetylase. Previous studies of mice carrying liver specific deletion of exon 4 of the Sirt1 gene revealed opposite responses of mutant mice to a high-fat diet in terms of fatty liver formation, which obscures the function of SRIT1 in liver development and lipid metabolism. To investigate this, we deleted exons 5 and 6 of Sirt1 in the liver by using a Cre-loxP approach. Western blot using an antibody to N-terminal SIRT1 does not detect a truncated protein in the liver of the mutant mice (Sirt1(flox5-6/flox5-6);Alb-Cre), suggesting a null mutation for SIRT1 is generated in the liver. Unlike the previously reported phenotypes, the Sirt1(flox5-6/flox5-6);Alb-Cre mice develop fatty liver under a normal feeding condition. The disease starts at two months of age and incidence increases as the animals become older, affecting 78% of them when they are over one year of age. We showed that the steatosis is accompanied by altered expression of a number of genes, including increased expression of ChREBP, which acts as one of the central determinants of lipid synthesis in the liver. This data uncovers an important role of SIRT1 in regulating lipid metabolism in the liver, and the SIRT1 mutant mice may serve as an animal model for studying human fatty liver disease and facilitate the development of effective therapeutic approach for the disease.
Keywords: ChREBP; SIRT1; SREBP-1c; fatty liver; mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lack of SIRT1 (Mammalian Sirtuin 1) activity leads to liver steatosis in the SIRT1+/- mice: a role of lipid mobilization and inflammation.Endocrinology. 2010 Jun;151(6):2504-14. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1013. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20339025 Free PMC article.
-
FABP4-Cre Mediated Expression of Constitutively Active ChREBP Protects Against Obesity, Fatty Liver, and Insulin Resistance.Endocrinology. 2015 Nov;156(11):4020-32. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1210. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 26248218 Free PMC article.
-
Salt-inducible kinase 2 links transcriptional coactivator p300 phosphorylation to the prevention of ChREBP-dependent hepatic steatosis in mice.J Clin Invest. 2010 Dec;120(12):4316-31. doi: 10.1172/JCI41624. Epub 2010 Nov 15. J Clin Invest. 2010. PMID: 21084751 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic steatosis: a role for de novo lipogenesis and the transcription factor SREBP-1c.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010 Oct;12 Suppl 2:83-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01275.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010. PMID: 21029304 Review.
-
[Can the hyperactivity of lipogenesis cause hepatic steatosis? A role for ChREBP].Med Sci (Paris). 2008 Oct;24(10):841-6. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20082410841. Med Sci (Paris). 2008. PMID: 18950580 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The Role of Neuregulin-1 in Steatotic and Non-Steatotic Liver Transplantation from Brain-Dead Donors.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 23;10(5):978. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10050978. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625715 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic sirtuin 1 is dispensable for fibrate-induced peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α function in vivo.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Apr 1;306(7):E824-37. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00175.2013. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24496310 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 Disruption in Human Fetal Hepatocytes Leads to Increased Accumulation of Glucose and Lipids.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 18;11(2):e0149344. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149344. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26890260 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol-induced liver injury is mediated via α4-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed in hepatocytes.Alcohol Clin Exp Res (Hoboken). 2025 Mar;49(3):515-525. doi: 10.1111/acer.15533. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Alcohol Clin Exp Res (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 39853711
-
Effect of fucoidan on ethanol-induced liver injury and steatosis in mice and the underlying mechanism.Food Nutr Res. 2021 Apr 20;65. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v65.5384. eCollection 2021. Food Nutr Res. 2021. PMID: 33994911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saunders LR, Verdin E. Sirtuins: critical regulators at the crossroads between cancer and aging. Oncogene. 2007;26:5489–5504. - PubMed
-
- Lavu S, Boss O, Elliott PJ. et al.Sirtuins--novel therapeutic targets to treat age-associated diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:841–853. - PubMed
-
- Guarente L. Sirtuins in aging and disease. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:483–488. - PubMed
-
- Vaquero A, Scher M, Erdjument-Bromage H. et al.SIRT1 regulates the histone methyl-transferase SUV39H1 during heterochromatin formation. Nature. 2007;450:440–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

