Human neutrophils do not express purinergic P2X7 receptors
- PMID: 21103213
- PMCID: PMC2947652
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-010-9178-7
Human neutrophils do not express purinergic P2X7 receptors
Abstract
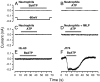
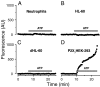
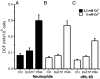
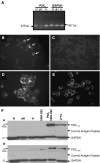
It has been reported that in human neutrophils, external ATP activates plasma membrane purinergic P2X(7) receptors (P2X(7)R) to elicit Ca(2+) entry, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), processing and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, shedding of adhesion molecules and uptake of large molecules. However, the expression of P2X(7)R at the plasma membrane of neutrophils has also been questioned since these putative responses are not always reproduced. In this work, we used electrophysiological recordings to measure functional responses associated with the activation of membrane receptors, spectrofluorometric measurements of ROS production and ethidium bromide uptake to asses coupling of P2X(7)R activation to downstream effectors, immune-labelling of P2X(7)R using a fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated antibody to detect the receptors at the plasma membrane, RT-PCR to determine mRNA expression of P2X(7)R and Western blot to determine protein expression in neutrophils and HL-60 cells. None of these assays reported the presence of P2X(7)R in the plasma membrane of neutrophils and non-differentiated or differentiated HL-60 cells-a model cell for human neutrophils. We concluded that P2X(7)R are not present at plasma membrane of human neutrophils and that the putative physiological responses triggered by external ATP should be reconsidered.
Keywords: Human; Neutrophils; Protein; Purinergic receptors; Whole cell current.
Figures
References
-
- Adrian K, Bernhard MK, Breitinger HG, Ogilvie A. Expression of purinergic receptors (ionotropic P2X1-7 and metabotropic P2Y1-11) during myeloid differentiation of HL60 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1492:127–138. - PubMed
-
- Axtell RA, Sandborg RR, Smolen JE, Ward PA, Boxer LA. Exposure of human neutrophils to exogenous nucleotides causes elevation in intracellular calcium, transmembrane calcium fluxes, and an alteration of a cytosolic factor resulting in enhanced superoxide production in response to FMLP and arachidonic acid. Blood. 1990;75:1324–1332. - PubMed
-
- Bass DA, Parce JW, Dechatelet LR, Szejda P, Seeds MC, Thomas M. Flow cytometric studies of oxidative product formation by neutrophils: a graded response to membrane stimulation. J Immunol. 1983;4:1910–1917. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

