The effects of P2X7 receptor antagonists on the formation and function of human osteoclasts in vitro
- PMID: 21103214
- PMCID: PMC2947658
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-010-9181-z
The effects of P2X7 receptor antagonists on the formation and function of human osteoclasts in vitro
Abstract
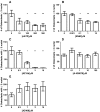
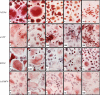
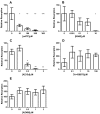
The P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) has been implicated in the process of multinucleation and cell fusion. We have previously demonstrated that blockade of P2X7Rs on osteoclast precursors using a blocking antibody inhibited multinucleated osteoclast formation in vitro, but that P2X7R KO mice maintain the ability to form multinucleated osteoclasts. This apparent contradiction of the role the P2X7R plays in multinucleation has prompted us to examine the effect of the most commonly used and recently available P2X7R antagonists on osteoclast formation and function. When added to recombinant RANKL and M-CSF human blood monocytes cultures, all but one compound, decreased the formation and function of multinucleated TRAP-positive osteoclasts in a concentration-dependent manner. These data provide further evidence for the role of the P2X7R in the formation of functional human multinucleated osteoclasts and highlight the importance of selection of antagonists for use in long-term experiments.
Keywords: ATP; Formation; Fusion; Osteoclast; P2 receptor; P2X7; Resorption.
Figures


References
-
- Rassendren F, Buell GN, Virginio C, Collo G, North RA, Surprenant A. The permeabilizing ATP receptor, P2X7. Cloning and expression of a human cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:5482–5486. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari D, Chiozzi P, Falzoni S, Dal Susino M, Melchiorri L, Baricordi OR, Virgilio F. Extracellular ATP triggers IL-1 beta release by activating the purinergic P2Z receptor of human macrophages. J Immunol. 1997;159:1451–1458. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

