Adult Kasabach-Merritt Syndrome due to Hepatic Giant Hemangioma
- PMID: 21103246
- PMCID: PMC2988922
- DOI: 10.1159/000242420
Adult Kasabach-Merritt Syndrome due to Hepatic Giant Hemangioma
Abstract
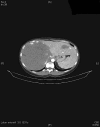
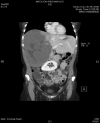
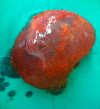
Cavernous hemangiomas are the most common benign tumors of the liver. They can reach enormous sizes and cause various complications. Kasabach-Merritt syndrome is a rare but serious complication characterized by consumptive coagulopathy caused by the hemangioma; mortality rate ranges between 10 and 37%. More than 80% of cases occur within the first year of life. Goals of the treatment are to control the coagulopathyand thrombocytopenia as well as to eradicate the hemangioma. Different nonsurgical treatment regimens are performed, includingsystemic corticosteroids, irradiation and various chemicals. Surgery should be limited to symptomatic or complicated cases. Although difficult, resection of the tumor is usually curative. Here we present a 44-year-old woman with giant hepatic hemangioma causing Kasabach-Merritt syndrome managed by enucleation.
Figures
References
-
- Hesselmann S, Micke O, Marquardt T, Baas S, Bramswig JH, Harms E, Willich N. Kasabach-Merritt syndrome: a review of the therapeutic options and a case report of successful treatment with radiotherapy and interferon alpha. Br J Radiol. 2002;75:180–184. - PubMed
-
- Brouty-Boye D, Zetter BR. Inhibition of cell motility by interferon. Science. 1980;208:516–518. - PubMed
-
- Lise M, Feltrin G, Da Pian PP, Miotto D, Pilati PL, Rubaltelli L, Zane D. Giant cavernous hemangiomas: diagnosis and surgical strategies. World J Surg. 1992;16:516–520. - PubMed
-
- Reischle S, Schuller-Petrovic S. Treatment of capillary hemangiomas of early childhood with a new method of cryosurgery. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42:809–813. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources