PI 3 kinase related kinases-independent proteolysis of BRCA1 regulates Rad51 recruitment during genotoxic stress in human cells
- PMID: 21103343
- PMCID: PMC2984446
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014027
PI 3 kinase related kinases-independent proteolysis of BRCA1 regulates Rad51 recruitment during genotoxic stress in human cells
Abstract
Background: The function of BRCA1 in response to ionizing radiation, which directly generates DNA double strand breaks, has been extensively characterized. However previous investigations have produced conflicting data on mutagens that initially induce other classes of DNA adducts. Because of the fundamental and clinical importance of understanding BRCA1 function, we sought to rigorously evaluate the role of this tumor suppressor in response to diverse forms of genotoxic stress.
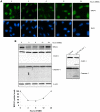
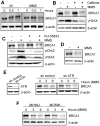
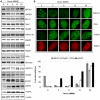
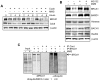
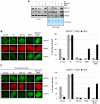
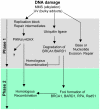
Methodology/principal findings: We investigated BRCA1 stability and localization in various human cells treated with model mutagens that trigger different DNA damage signaling pathways. We established that, unlike ionizing radiation, either UVC or methylmethanesulfonate (MMS) (generating bulky DNA adducts or alkylated bases respectively) induces a transient downregulation of BRCA1 protein which is neither prevented nor enhanced by inhibition of PIKKs. Moreover, we found that the proteasome mediates early degradation of BRCA1, BARD1, BACH1, and Rad52 implying that critical components of the homologous recombination machinery need to be functionally abrogated as part of the early response to UV or MMS. Significantly, we found that inhibition of BRCA1/BARD1 downregulation is accompanied by the unscheduled recruitment of both proteins to chromatin along with Rad51. Consistently, treatment of cells with MMS engendered complete disassembly of Rad51 from pre-formed ionizing radiation-induced foci. Following the initial phase of BRCA1/BARD1 downregulation, we found that the recovery of these proteins in foci coincides with the formation of RPA and Rad51 foci. This indicates that homologous recombination is reactivated at later stage of the cellular response to MMS, most likely to repair DSBs generated by replication blocks.
Conclusion/significance: Taken together our results demonstrate that (i) the stabilities of BRCA1/BARD1 complexes are regulated in a mutagen-specific manner, and (ii) indicate the existence of mechanisms that may be required to prevent the simultaneous recruitment of conflicting signaling pathways to sites of DNA damage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
RNF8 regulates assembly of RAD51 at DNA double-strand breaks in the absence of BRCA1 and 53BP1.Cancer Res. 2012 Oct 1;72(19):4974-83. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1057. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22865450
-
BRCA1 recruitment to damaged DNA sites is dependent on CDK9.Cell Cycle. 2017 Apr 3;16(7):665-672. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1295177. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28278048 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA1-BARD1 complexes are required for p53Ser-15 phosphorylation and a G1/S arrest following ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 23;279(30):31251-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405372200. Epub 2004 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15159397
-
Involvement of DNA-PK and ATM in radiation- and heat-induced DNA damage recognition and apoptotic cell death.J Radiat Res. 2010;51(5):493-501. doi: 10.1269/jrr.10039. Epub 2010 Aug 28. J Radiat Res. 2010. PMID: 20814172 Review.
-
BRCA1/BARD1 is a nucleosome reader and writer.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Jul;47(7):582-595. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.03.001. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35351360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antitumor activity of NVP-BKM120--a selective pan class I PI3 kinase inhibitor showed differential forms of cell death based on p53 status of glioma cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 1;18(1):184-95. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1558. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22065080 Free PMC article.
-
Undetectable histone O-GlcNAcylation in mammalian cells.Epigenetics. 2015;10(8):677-91. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1060387. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26075789 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor and deubiquitinase BAP1 promotes DNA double-strand break repair.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 7;111(1):285-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1309085110. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24347639 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer 1 (BRCA1)-deficient embryos develop normally but are more susceptible to ethanol-initiated DNA damage and embryopathies.Redox Biol. 2016 Apr;7:30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Redox Biol. 2016. PMID: 26629949 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Personalized Metabolic Signatures in Breast Cancer.Metabolites. 2020 Dec 30;11(1):20. doi: 10.3390/metabo11010020. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 33396819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Narod SA, Foulkes WD. BRCA1 and BRCA2: 1994 and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:665–676. - PubMed
-
- Xu B, O'Donnell AH, Kim ST, Kastan MB. Phosphorylation of serine 1387 in Brca1 is specifically required for the Atm-mediated S-phase checkpoint after ionizing irradiation. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4588–4591. - PubMed
-
- Cortez D, Wang Y, Qin J, Elledge SJ. Requirement of ATM-dependent phosphorylation of brca1 in the DNA damage response to double-strand breaks. Science. 1999;286:1162–1166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

