Elastin peptides signaling relies on neuraminidase-1-dependent lactosylceramide generation
- PMID: 21103358
- PMCID: PMC2982818
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014010
Elastin peptides signaling relies on neuraminidase-1-dependent lactosylceramide generation
Abstract
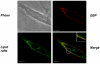
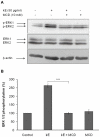
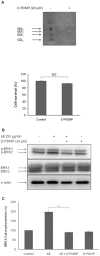
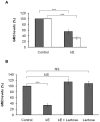
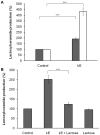
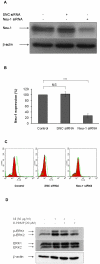
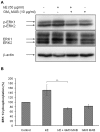
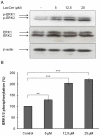
The sialidase activity of neuraminidase-1 (Neu-1) is responsible for ERK 1/2 pathway activation following binding of elastin peptide on the elastin receptor complex. In this work, we demonstrate that the receptor and lipid rafts colocalize at the plasma membrane. We also show that the disruption of these microdomains as well as their depletion in glycolipids blocks the receptor signaling. Following elastin peptide treatment, the cellular GM(3) level decreases while lactosylceramide (LacCer) content increases consistently with a GM(3)/LacCer conversion. The use of lactose or Neu-1 siRNA blocks this process suggesting that the elastin receptor complex is responsible for this lipid conversion. Flow cytometry analysis confirms this elastin peptide-driven LacCer generation. Further, the use of a monoclonal anti-GM(3) blocking antibody shows that GM(3) is required for signaling. In conclusion, our data strongly suggest that Neu-1-dependent GM(3)/LacCer conversion is the key event leading to signaling by the elastin receptor complex. As a consequence, we propose that LacCer is an early messenger for this receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Uncoupling of Elastin Complex Receptor during In Vitro Aging Is Related to Modifications in Its Intrinsic Sialidase Activity and the Subsequent Lactosylceramide Production.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 18;10(6):e0129994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129994. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26086247 Free PMC article.
-
The elastin receptor complex transduces signals through the catalytic activity of its Neu-1 subunit.J Biol Chem. 2007 Apr 27;282(17):12484-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M609505200. Epub 2007 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17327233
-
Lactosylceramide-enriched glycosphingolipid signaling domain mediates superoxide generation from human neutrophils.Blood. 2002 Aug 15;100(4):1454-64. Blood. 2002. PMID: 12149231
-
Organization and functions of glycolipid-enriched microdomains in phagocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jan;1851(1):90-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 24968752 Review.
-
Involvement of glycosphingolipid-enriched lipid rafts in inflammatory responses.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2015 Jan 1;20(2):325-34. doi: 10.2741/4312. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2015. PMID: 25553454 Review.
Cited by
-
Positive regulation of insulin signaling by neuraminidase 1.Diabetes. 2013 Jul;62(7):2338-46. doi: 10.2337/db12-1825. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23520133 Free PMC article.
-
The hypothesis on function of glycosphingolipids and ABO blood groups revisited.Neurochem Res. 2012 Jun;37(6):1170-84. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0734-0. Epub 2012 Mar 11. Neurochem Res. 2012. PMID: 22407244 Review.
-
Uncoupling of Elastin Complex Receptor during In Vitro Aging Is Related to Modifications in Its Intrinsic Sialidase Activity and the Subsequent Lactosylceramide Production.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 18;10(6):e0129994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129994. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26086247 Free PMC article.
-
Neuraminidase-1: A Sialidase Involved in the Development of Cancers and Metabolic Diseases.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 5;14(19):4868. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194868. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elastin-Derived VGVAPG Fragment Decorated Cell-Penetrating Peptide with Improved Gene Delivery Efficacy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 16;15(2):670. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020670. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kielty CM, Sherratt MJ, Shuttleworth CA. Elastic fibres. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:2817–2828. - PubMed
-
- Duca L, Floquet N, Alix AJ, Haye B, Debelle L. Elastin as a matrikine. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2004;49:235–244. - PubMed
-
- Ooyama T, Fukuda K, Oda H, Nakamura H, Hikita Y. Substratum-bound elastin peptide inhibits aortic smooth muscle cell migration in vitro. Arteriosclerosis. 1987;7:593–598. - PubMed
-
- Mecham RP, Hinek A, Griffin GL, Senior RM, Liotta LA. The elastin receptor shows structural and functional similarities to the 67-kDa tumor cell laminin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:16652–16657. - PubMed
-
- Ghuysen-Itard AF, Robert L, Jacob MP. [Effect of elastin peptides on cell proliferation]. C R Acad Sci III. 1992;315:473–478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

