The ubiquitin ligase Ubr2, a recognition E3 component of the N-end rule pathway, stabilizes Tex19.1 during spermatogenesis
- PMID: 21103378
- PMCID: PMC2982839
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014017
The ubiquitin ligase Ubr2, a recognition E3 component of the N-end rule pathway, stabilizes Tex19.1 during spermatogenesis
Abstract
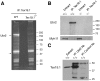
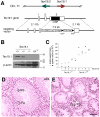
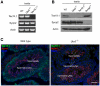
Ubiquitin E3 ligases target their substrates for ubiquitination, leading to proteasome-mediated degradation or altered biochemical properties. The ubiquitin ligase Ubr2, a recognition E3 component of the N-end rule proteolytic pathway, recognizes proteins with N-terminal destabilizing residues and plays an important role in spermatogenesis. Tex19.1 (also known as Tex19) has been previously identified as a germ cell-specific protein in mouse testis. Here we report that Tex19.1 forms a stable protein complex with Ubr2 in mouse testes. The binding of Tex19.1 to Ubr2 is independent of the second position cysteine of Tex19.1, a putative target for arginylation by the N-end rule pathway R-transferase. The Tex19.1-null mouse mutant phenocopies the Ubr2-deficient mutant in three aspects: heterogeneity of spermatogenic defects, meiotic chromosomal asynapsis, and embryonic lethality preferentially affecting females. In Ubr2-deficient germ cells, Tex19.1 is transcribed, but Tex19.1 protein is absent. Our results suggest that the binding of Ubr2 to Tex19.1 metabolically stabilizes Tex19.1 during spermatogenesis, revealing a new function for Ubr2 outside the conventional N-end rule pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
UBR2 of the N-end rule pathway is required for chromosome stability via histone ubiquitylation in spermatocytes and somatic cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37414. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037414. Epub 2012 May 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22616001 Free PMC article.
-
Female lethality and apoptosis of spermatocytes in mice lacking the UBR2 ubiquitin ligase of the N-end rule pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Nov;23(22):8255-71. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.22.8255-8271.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14585983 Free PMC article.
-
Tex19.1 promotes Spo11-dependent meiotic recombination in mouse spermatocytes.PLoS Genet. 2017 Jul 14;13(7):e1006904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006904. eCollection 2017 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28708824 Free PMC article.
-
The role of E3 ligases in the ubiquitin-dependent regulation of spermatogenesis.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Jun;30:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24632385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microtubular TRIM36 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase in Embryonic Development and Spermatogenesis.Cells. 2022 Jan 12;11(2):246. doi: 10.3390/cells11020246. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35053362 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Defects in meiotic recombination delay progression through pachytene in Tex19.1-/- mouse spermatocytes.Chromosoma. 2018 Dec;127(4):437-459. doi: 10.1007/s00412-018-0674-9. Epub 2018 Jun 16. Chromosoma. 2018. PMID: 29907896 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing N-terminal Arginylation through the Use of Peptide Arrays and Degradation Assays.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 30;291(40):20976-20992. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.747956. Epub 2016 Aug 10. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27510035 Free PMC article.
-
UBR2 of the N-end rule pathway is required for chromosome stability via histone ubiquitylation in spermatocytes and somatic cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37414. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037414. Epub 2012 May 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22616001 Free PMC article.
-
Tex19.1 inhibits the N-end rule pathway and maintains acetylated SMC3 cohesin and sister chromatid cohesion in oocytes.J Cell Biol. 2020 May 4;219(5):e201702123. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201702123. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32232464 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic gene activation in somatic and germ cell tumours.Andrology. 2019 Jul;7(4):415-427. doi: 10.1111/andr.12628. Epub 2019 May 17. Andrology. 2019. PMID: 31102330 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bachmair A, Finley D, Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986;234(4773):179–186. - PubMed
-
- Tasaki T, Kwon YT. The mammalian N-end rule pathway: New insights into its components and physiological roles. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007;32(11):520–528. - PubMed
-
- Hu RG, Sheng J, Qi X, Xu Z, Takahashi TT, et al. The N-end rule pathway as a nitric oxide sensor controlling the levels of multiple regulators. Nature. 2005;437(7061):981–986. - PubMed
-
- Kwon YT, Kashina AS, Davydov IV, Hu RG, An JY, et al. An essential role of N-terminal arginylation in cardiovascular development. Science. 2002;297(5578):96–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

