Gender differences in S-nitrosoglutathione reductase activity in the lung
- PMID: 21103380
- PMCID: PMC2982841
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014007
Gender differences in S-nitrosoglutathione reductase activity in the lung
Abstract
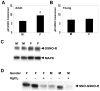
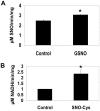
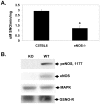
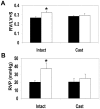
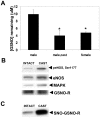
S-nitrosothiols have been implicated in the etiology of various pulmonary diseases. Many of these diseases display gender preferences in presentation or altered severity that occurs with puberty, the mechanism by which is unknown. Estrogen has been shown to influence the expression and activity of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) which is associated with increased S-nitrosothiol production. The effects of gender hormones on the expression and activity of the de-nitrosylating enzyme S-nitrosoglutathione reductase (GSNO-R) are undefined. This report evaluates the effects of gender hormones on the activity and expression of GSNO-R and its relationship to N-acetyl cysteine (NAC)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH). GSNO-R activity was elevated in lung homogenates from female compared to male mice. Increased activity was not due to changes in GSNO-R expression, but correlated with GSNO-R S-nitrosylation: females were greater than males. The ability of GSNO-R to be activated by S-nitrosylation was confirmed by: 1) the ability of S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) to increase the activity of GSNO-R in murine pulmonary endothelial cells and 2) reduced activity of GSNO-R in lung homogenates from eNOS(-/-) mice. Gender differences in GSNO-R activity appear to explain the difference in the ability of NAC to induce PH: female and castrated male animals are protected from NAC-induced PH. Castration results in elevated GSNO-R activity that is similar to that seen in female animals. The data suggest that GSNO-R activity is modulated by both estrogens and androgens in conjunction with hormonal regulation of eNOS to maintain S-nitrosothiol homeostasis. Moreover, disruption of this eNOS-GSNO-R axis contributes to the development of PH.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Benhar M, Forrester MT, Stamler JS. Protein denitrosylation: enzymatic mechanisms and cellular functions. Nature Reviews. 2009;10:721–732. - PubMed
-
- Haqqani AS, Do SK, Birnboim HC. The role of a formaldehyde dehydrogenase-glutathione pathway in protein S-nitrosylation in mammalian cells. Nitric Oxide. 2003;9:172–181. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Hausladen A, Zeng M, Que L, Heitman J, et al. A metabolic enzyme for S-nitrosothiol conserved from bacteria to humans. Nature. 2001;410:490–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

