Population genomic analysis of a bacterial plant pathogen: novel insight into the origin of Pierce's disease of grapevine in the U.S
- PMID: 21103383
- PMCID: PMC2982844
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015488
Population genomic analysis of a bacterial plant pathogen: novel insight into the origin of Pierce's disease of grapevine in the U.S
Abstract
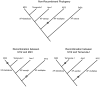
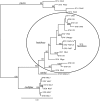
Invasive diseases present an increasing problem worldwide; however, genomic techniques are now available to investigate the timing and geographical origin of such introductions. We employed genomic techniques to demonstrate that the bacterial pathogen causing Pierce's disease of grapevine (PD) is not native to the US as previously assumed, but descended from a single genotype introduced from Central America. PD has posed a serious threat to the US wine industry ever since its first outbreak in Anaheim, California in the 1880s and continues to inhibit grape cultivation in a large area of the country. It is caused by infection of xylem vessels by the bacterium Xylella fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa, a genetically distinct subspecies at least 15,000 years old. We present five independent kinds of evidence that strongly support our invasion hypothesis: 1) a genome-wide lack of genetic variability in X. fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa found in the US, consistent with a recent common ancestor; 2) evidence for historical allopatry of the North American subspecies X. fastidiosa subsp. multiplex and X. fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa; 3) evidence that X. fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa evolved in a more tropical climate than X. fastidiosa subsp. multiplex; 4) much greater genetic variability in the proposed source population in Central America, variation within which the US genotypes are phylogenetically nested; and 5) the circumstantial evidence of importation of known hosts (coffee plants) from Central America directly into southern California just prior to the first known outbreak of the disease. The lack of genetic variation in X. fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa in the US suggests that preventing additional introductions is important since new genetic variation may undermine PD control measures, or may lead to infection of other crop plants through the creation of novel genotypes via inter-subspecific recombination. In general, geographically mixing of previously isolated subspecies should be avoided.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Pimentel D, Zuniga R, Morrison D. Update on the environmental and economic costs associated with alien-invasive species in the United States. Ecol Econ. 2005;52:273–288.
-
- Pierce NB. Washington: Government Printing Office; 1892. The California vine disease.A preliminary report of investigations. US Department of Agriculture. Division of vegetable pathology bulletin 2.
-
- Stoner WN. A comparison between grape degeneration in florida and Pierce's disease in California. Florida Entomol. 1952;35:62–68.
-
- Hewitt WB. The probable home of Pierce's disease virus. Plant Disease Reporter. 1958;42:211–215.
-
- Purcell AH, Hopkins DL. Fastidious xylem-limited bacterial plant pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 1996;34:131–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

