Insulin promoter DNA methylation correlates negatively with insulin gene expression and positively with HbA(1c) levels in human pancreatic islets
- PMID: 21104225
- PMCID: PMC3017313
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-010-1967-6
Insulin promoter DNA methylation correlates negatively with insulin gene expression and positively with HbA(1c) levels in human pancreatic islets
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Although recent studies propose that epigenetic factors influence insulin expression, the regulation of the insulin gene in type 2 diabetic islets is still not fully understood. Here, we examined DNA methylation of the insulin gene promoter in pancreatic islets from patients with type 2 diabetes and non-diabetic human donors and related it to insulin expression, HbA(1c) levels, BMI and age.
Methods: DNA methylation was analysed in 25 CpG sites of the insulin promoter and insulin mRNA expression was analysed using quantitative RT-PCR in pancreatic islets from nine donors with type 2 diabetes and 48 non-diabetic donors.
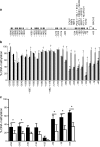
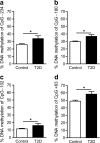
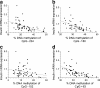
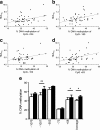
Results: Insulin mRNA expression (p = 0.002), insulin content (p = 0.004) and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (p = 0.04) were reduced in pancreatic islets from patients with type 2 diabetes compared with non-diabetic donors. Moreover, four CpG sites located 234 bp, 180 and 102 bp upstream and 63 bp downstream of the transcription start site (CpG -234, -180, -102 and +63, respectively), showed increased DNA methylation in type 2 diabetic compared with non-diabetic islets (7.8%, p = 0.03; 7.1%, p = 0.02; 4.4%, p = 0.03 and 9.3%, p = 0.03, respectively). While insulin mRNA expression correlated negatively (p < 1 × 10(-6)), the level of HbA(1c) correlated positively (p ≤ 0.01) with the degree of DNA methylation for CpG -234, -180 and +63. Furthermore, DNA methylation for nine additional CpG sites correlated negatively with insulin mRNA expression (p ≤ 0.01). Also, exposure to hyperglycaemia for 72 h increased insulin promoter DNA methylation in clonal rat beta cells (p = 0.005).
Conclusions/interpretations: This study demonstrates that DNA methylation of the insulin promoter is increased in patients with type 2 diabetes and correlates negatively with insulin gene expression in human pancreatic islets.
Figures
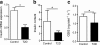
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

