Catecholamine storage vesicles: role of core protein genetic polymorphisms in hypertension
- PMID: 21104344
- PMCID: PMC3016145
- DOI: 10.1007/s11906-010-0170-y
Catecholamine storage vesicles: role of core protein genetic polymorphisms in hypertension
Abstract
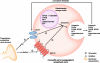
Hypertension is a complex trait with deranged autonomic control of the circulation. The sympathoadrenal system exerts minute-to-minute control over cardiac output and vascular tone. Catecholamine storage vesicles (or chromaffin granules) of the adrenal medulla contain remarkably high concentrations of chromogranins/secretogranins (or "granins"), catecholamines, neuropeptide Y, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and Ca(2+). Within secretory granules, granins are co-stored with catecholamine neurotransmitters and co-released upon stimulation of the regulated secretory pathway. The principal granin family members, chromogranin A (CHGA), chromogranin B (CHGB), and secretogranin II (SCG2), may have evolved from shared ancestral exons by gene duplication. This article reviews human genetic variation at loci encoding the major granins and probes the effects of such polymorphisms on blood pressure, using twin pairs to probe heritability and individuals with the most extreme blood pressure values in the population to study hypertension.
Figures
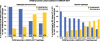
Similar articles
-
Pleiotropic effects of novel trans-acting loci influencing human sympathochromaffin secretion.Physiol Genomics. 2006 May 16;25(3):470-9. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00295.2005. Epub 2006 Mar 22. Physiol Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16554546
-
Naturally occurring human genetic variation in the 3'-untranslated region of the secretory protein chromogranin A is associated with autonomic blood pressure regulation and hypertension in a sex-dependent fashion.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Oct 28;52(18):1468-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.07.047. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 19017515 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread occurrence of chromogranins/secretogranins in the matrix of secretory granules of endocrinologically silent pituitary adenomas.J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Apr;40(4):523-33. doi: 10.1177/40.4.1552186. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992. PMID: 1552186
-
Catecholamine storage vesicles and the metabolic syndrome: The role of the chromogranin A fragment pancreastatin.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006 Nov;8(6):621-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2006.00575.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006. PMID: 17026486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromogranins A and B and secretogranin II: evolutionary and functional aspects.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2008 Feb;192(2):309-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2007.01806.x. Epub 2007 Nov 15. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2008. PMID: 18005393 Review.
Cited by
-
The granin VGF promotes genesis of secretory vesicles, and regulates circulating catecholamine levels and blood pressure.FASEB J. 2014 May;28(5):2120-33. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-239509. Epub 2014 Feb 4. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24497580 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism for Hypertensive Renal Disease: Differential Regulation of Chromogranin A Expression at 3'-Untranslated Region Polymorphism C+87T by MicroRNA-107.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Aug;26(8):1816-25. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014060537. Epub 2014 Nov 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25392232 Free PMC article.
-
The surging role of Chromogranin A in cardiovascular homeostasis.Front Chem. 2014 Aug 14;2:64. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2014.00064. eCollection 2014. Front Chem. 2014. PMID: 25177680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Variants in Transcription Factor Binding Sites in Humans: Triggered by Natural Selection and Triggers of Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 18;22(8):4187. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084187. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pGlu-serpinin protects the normotensive and hypertensive heart from ischemic injury.J Endocrinol. 2015 Dec;227(3):167-178. doi: 10.1530/JOE-15-0199. Epub 2015 Sep 23. J Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26400960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Videen JS, Mezger MS, Chang YM, O’Connor DT. Calcium and catecholamine interactions with adrenal chromogranins. Comparison of driving forces in binding and aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:3066–3073. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

