Ups and downs of alcohol use among first-year college students: Number of drinks, heavy drinking, and stumble and pass out drinking days
- PMID: 21106298
- PMCID: PMC3018543
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2010.10.005
Ups and downs of alcohol use among first-year college students: Number of drinks, heavy drinking, and stumble and pass out drinking days
Abstract
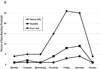
Given the dynamic fluctuating nature of alcohol use among emerging adults (Del Boca, Darkes, Greenbaum, & Goldman, 2004), patterns of alcohol use were modeled across 70 days in an intensive repeated-measures diary design. Two hundred first-year college students provided 10 weekly reports of their daily alcohol consumption via computer-assisted telephone interviews. Multi-level models demonstrated large within-person variability across days in drinks consumed, binge drinking, and days exceeding self-reported limits for stumbling around and passing out; these outcome variables were predicted by weekdays vs. weekend days (within-person) and gender, age of drinking initiation, fraternity/sorority membership, and alcohol motivations (between-persons). Repeated measurement of alternate indicators of alcohol use permits the examination of novel and important questions about alcohol use and abuse particularly in young adult and other erratically drinking populations.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bachman JG, Wadsworth KN, O’Malley PM, Johnston LD, Schulenberg J. Smoking, drinking and drug use in young adulthood: The impact of new freedoms and new responsibilities. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum; 1997.
-
- Chassin L, Pitts SC, Prost J. Binge drinking trajectories from adolescence to emerging adulthood in a high-risk sample: Predictors and substance abuse outcomes. Health Psychology. 2002;70:67–78. - PubMed
-
- Chou SP, Pickering RP. Early onset of drinking as a risk factor for lifetime alcohol-related problems. British Journal of Addiction. 1992;87:1199–1204. - PubMed
-
- DeJong W, Langford LM. A typology for campus-based alcohol prevention: Moving toward environmental management strategies. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 2002 Supplement No. 14:140–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical