The Spectrum projection package: improvements in estimating incidence by age and sex, mother-to-child transmission, HIV progression in children and double orphans
- PMID: 21106510
- PMCID: PMC3173821
- DOI: 10.1136/sti.2010.044222
The Spectrum projection package: improvements in estimating incidence by age and sex, mother-to-child transmission, HIV progression in children and double orphans
Abstract
Background: The Spectrum program is used to estimate key HIV indicators from the trends in incidence and prevalence estimated by the Estimation and Projection Package or the Workbook. These indicators include the number of people living with HIV, new infections, AIDS deaths, AIDS orphans, the number of adults and children needing treatment, the need for prevention of mother-to-child transmission and the impact of antiretroviral treatment on survival. The UNAIDS Reference Group on Estimates, Models and Projections regularly reviews new data and information needs, and recommends updates to the methodology and assumptions used in Spectrum.
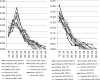
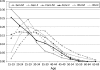
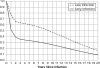
Methods: The latest update to Spectrum was used in the 2009 round of global estimates. This update contains new procedures for estimating: the age and sex distribution of adult incidence, new child infections occurring around delivery or through breastfeeding, the survival of children by timing of infection and the number of double orphans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Stover J. AIM: A Computer Program for Making HIV/AIDS Projections And Examining The Demographic and Social Impacts Of AIDS. Glastonbury CT: Futures Institute, 2009. http://www.FuturesInstitute.org and http://www.unaids.org
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
