Under-5 mortality due to HIV: regional levels and 1990-2009 trends
- PMID: 21106516
- PMCID: PMC3173825
- DOI: 10.1136/sti.2010.046201
Under-5 mortality due to HIV: regional levels and 1990-2009 trends
Abstract
Background: Since at least the late 1990s, HIV has been viewed as a major threat to efforts by countries to reduce under-5 mortality. Previous work has documented increased under-5 mortality due to HIV from 1990 to 1999 in Africa. The current analysis presents estimates and trends in under-5 mortality due to HIV in low- and middle-income countries by region up to 2009.
Methods: The analyses are based on the national models of HIV and AIDS produced by country teams in coordination with UNAIDS and its partners for the years 1990-2009. These models produce a time series of estimates of HIV-related mortality as well as overall mortality in children aged <5 years.
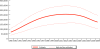
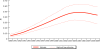
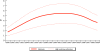
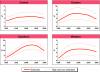
Results and conclusion: These analyses indicate that, in 2009, HIV accounted for roughly 2.1% (1.2-3.0%) of under-5 deaths in low- and middle-income countries and 3.6% (2.0-5.0%) in sub-Saharan Africa. The percentage of under-5 deaths due to HIV has been falling in the last decade--for example, from 2.6% (1.6-3.5%) in 2000 to 2.1% (1.2-3.0%) in 2009 in low- and middle-income countries and from 5.4% (3.3-7.3%) in 2000 to 3.6% (2.0-5.0%) in 2009 in sub-Saharan Africa. This fall in the percentage of under-5 deaths due to HIV has been driven by a combination of factors including scale-up of prevention of mother-to-child transmission programmes and treatment for pregnant women and children, as well as a decrease in the prevalence of HIV among pregnant women.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simplified antiviral prophylaxis with or and without artificial feeding to reduce mother-to-child transmission of HIV in low and middle income countries: modelling positive and negative impact on child survival.Med Sci Monit. 2001 Sep-Oct;7(5):1043-51. Med Sci Monit. 2001. PMID: 11535956
-
Meeting international goals in child survival and HIV/AIDS.Lancet. 2002 Jul 27;360(9329):284-9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)09550-8. Lancet. 2002. PMID: 12147371
-
Divergences in trends in child and adult mortality in sub-Saharan Africa: survey evidence on the survival of children and siblings.Popul Stud (Camb). 2014;68(2):161-77. doi: 10.1080/00324728.2013.856458. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Popul Stud (Camb). 2014. PMID: 24303913
-
Operational issues and barriers to implementation of prevention of mother-to-child transmission of HIV (PMTCT) interventions in Sub-Saharan Africa.Curr HIV Res. 2013 Mar;11(2):144-59. doi: 10.2174/1570162x11311020007. Curr HIV Res. 2013. PMID: 23432490 Review.
-
[The UN Millennium Project; especially the prevention and treatment of the HIV-virus and AIDS in order to reduce child and maternal mortality].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2006 Jun 24;150(25):1413-7. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2006. PMID: 16841592 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Under-five mortality and maternal HIV status in Tanzania: analysis of trends between 2003 and 2012 using AIDS Indicator Survey data.Glob Health Action. 2016 Jun 20;9:31676. doi: 10.3402/gha.v9.31676. eCollection 2016. Glob Health Action. 2016. PMID: 27329937 Free PMC article.
-
Derivation of parameters used in Spectrum for eligibility for antiretroviral therapy and survival on antiretroviral therapy.Sex Transm Infect. 2010 Dec;86 Suppl 2(Suppl_2):ii28-34. doi: 10.1136/sti.2010.044255. Sex Transm Infect. 2010. PMID: 21106512 Free PMC article.
-
Under-two child mortality according to maternal HIV status in Rwanda: assessing outcomes within the National PMTCT Program.Pan Afr Med J. 2011;9:37. doi: 10.4314/pamj.v9i1.71215. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Pan Afr Med J. 2011. PMID: 22145068 Free PMC article.
-
Young children's probability of dying before and after their mother's death: a rural South African population-based surveillance study.PLoS Med. 2013;10(3):e1001409. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001409. Epub 2013 Mar 26. PLoS Med. 2013. PMID: 23555200 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-free survival among nine- to 24-month-old children born to HIV-positive mothers in the Rwandan national PMTCT programme: a community-based household survey.J Int AIDS Soc. 2012 Jan 30;15(1):4. doi: 10.1186/1758-2652-15-4. J Int AIDS Soc. 2012. PMID: 22289641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS. New York: United Nations, 2001:25–7
-
- Murray CJ, Laakso T, Shibuya K, et al. Can we achieve Millennium Development Goal 4? New analysis of country trends and forecasts of under-5 mortality to 2015. Lancet 2007;370:1040–54 - PubMed
-
- Bryce J, Boschi-Pinto C, Shibuya K, et al. WHO estimates of the causes of death in children. Lancet 2005;365:1147–52 - PubMed
-
- Black RE, Cousens S, Johnson HL, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2008: a systematic analysis. Lancet 2010;375:1969–87 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
