Arrestin-2 differentially regulates PAR4 and ADP receptor signaling in platelets
- PMID: 21106537
- PMCID: PMC3030382
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.118018
Arrestin-2 differentially regulates PAR4 and ADP receptor signaling in platelets
Abstract
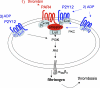
Arrestins can facilitate desensitization or signaling by G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) in many cells, but their roles in platelets remain uncharacterized. Because of recent reports that arrestins can serve as scaffolds to recruit phosphatidylinositol-3 kinases (PI3K)s to GPCRs, we sought to determine whether arrestins regulate PI3K-dependent Akt signaling in platelets, with consequences for thrombosis. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments demonstrate that arrestin-2 associates with p85 PI3Kα/β subunits in thrombin-stimulated platelets, but not resting cells. The association is inhibited by inhibitors of P2Y12 and Src family kinases (SFKs). The function of arrestin-2 in platelets is agonist-specific, as PAR4-dependent Akt phosphorylation and fibrinogen binding were reduced in arrestin-2 knock-out platelets compared with WT controls, but ADP-stimulated signaling to Akt and fibrinogen binding were unaffected. ADP receptors regulate arrestin recruitment to PAR4, because co-immunoprecipitates of arrestin-2 with PAR4 are disrupted by inhibitors of P2Y1 or P2Y12. P2Y1 may regulate arrestin-2 recruitment to PAR4 through protein kinase C (PKC) activation, whereas P2Y12 directly interacts with PAR4 and therefore, may help to recruit arrestin-2 to PAR4. Finally, arrestin2(-/-) mice are less sensitive to ferric chloride-induced thrombosis than WT mice, suggesting that arrestin-2 can regulate thrombus formation in vivo. In conclusion, arrestin-2 regulates PAR4-dependent signaling pathways, but not responses to ADP alone, and contributes to thrombus formation in vivo.
Figures








References
-
- Reiter E., Lefkowitz R. J. (2006) Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 17, 159–165 - PubMed
-
- DeWire S. M., Ahn S., Lefkowitz R. J., Shenoy S. K. (2007) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 69, 483–510 - PubMed
-
- Luttrell L. M., Ferguson S. S., Daaka Y., Miller W. E., Maudsley S., Della Rocca G. J., Lin F., Kawakatsu H., Owada K., Luttrell D. K., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. (1999) Science 283, 655–661 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

