Twenty-four-hour profiles of acylated and total ghrelin: relationship with glucose levels and impact of time of day and sleep
- PMID: 21106712
- PMCID: PMC3206394
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2010-1978
Twenty-four-hour profiles of acylated and total ghrelin: relationship with glucose levels and impact of time of day and sleep
Abstract
Context: The acylation of ghrelin is essential for its stimulatory effects on GH release and appetite. Most of the physiology of ghrelin has been defined based on the assay of total ghrelin (TG), which mainly reflects levels of unacylated ghrelin. Whether levels of acylated ghrelin (AG) are influenced by circadian time and sleep and impact glucose regulation under physiologic conditions is not known.
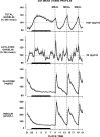
Methods: Blood was sampled at 10- to 30-min intervals for 24 h in 14 healthy young lean men under controlled conditions of activity, light-dark cycle, and sleep-wake schedule. The subjects ingested three identical carbohydrate-rich meals at 5-h intervals. Sleep was polygraphically monitored. Levels of TG and AG were measured by RIA. The 24-h profiles of glucose and insulin levels were assessed simultaneously.
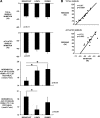
Results: Postprandial glucose concentrations were positively correlated with mean levels of AG but not TG, independently of insulin. Postprandial suppression and rebound of AG and TG occurred in parallel and were not impacted by time of day. The nocturnal elevation of AG and TG reflects the postdinner rebound curbed by an inhibitory effect of sleep. The ratio of AG to TG was lower during sleep than during wake, consistent with a reduction of orexigenic signal.
Conclusions: Individual differences in AG levels may be an important predictor of overall glucose control under physiological conditions. Sleep, but not time of day, impacts postprandial TG and AG responses. The inhibitory effect of sleep on ghrelin release and acylation is consistent with the association between sleeping and fasting.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Intravenous lipid infusion and total plasma fatty acids positively modulate plasma acylated ghrelin in vivo.Clin Nutr. 2017 Jun;36(3):775-781. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.05.017. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Clin Nutr. 2017. PMID: 27312085
-
Influence of age, gender, and glucose tolerance on fasting and fed acylated ghrelin in Prader Willi syndrome.Clin Nutr. 2009 Feb;28(1):94-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2008.12.002. Epub 2009 Jan 17. Clin Nutr. 2009. PMID: 19150743 Clinical Trial.
-
Basal and postprandial plasma levels of PYY, ghrelin, cholecystokinin, gastrin and insulin in women with moderate and morbid obesity and metabolic syndrome.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007 Mar;58 Suppl 1:13-35. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17443025
-
The effect of acute exercise on pre-prandial ghrelin levels in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Peptides. 2021 Nov;145:170625. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2021.170625. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Peptides. 2021. PMID: 34391825 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of hypoxia on hunger perceptions, appetite-related hormone concentrations and energy intake: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Appetite. 2018 Jun 1;125:98-108. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2018.01.015. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Appetite. 2018. PMID: 29374575
Cited by
-
Connecting insufficient sleep and insomnia with metabolic dysfunction.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2023 Jan;1519(1):94-117. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14926. Epub 2022 Nov 13. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2023. PMID: 36373239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic disturbances: role of the circadian timing system and sleep.Diabetol Int. 2016 Jul 19;8(1):14-22. doi: 10.1007/s13340-016-0279-6. eCollection 2017 Mar. Diabetol Int. 2016. PMID: 30603302 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian rhythm of circulating levels of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Jan;100(1):220-6. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-3455. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 25368979 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep and obesity.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011 Jul;14(4):402-12. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283479109. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011. PMID: 21659802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shifting the circadian rhythm of feeding in mice induces gastrointestinal, metabolic and immune alterations which are influenced by ghrelin and the core clock gene Bmal1.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 16;9(10):e110176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110176. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25329803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K. 1999. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402:656–660 - PubMed
-
- van der Lely AJ. 2009. Ghrelin and new metabolic frontiers. Horm Res 71(Suppl 1):129–133 - PubMed
-
- Gasco V, Beccuti G, Marotta F, Benso A, Granata R, Broglio F, Ghigo E. 2010. Endocrine and metabolic actions of ghrelin. Endocr Dev 17:86–95 - PubMed
-
- Granata R, Baragli A, Settanni F, Scarlatti F, Ghigo E. 2010. Unraveling the role of the ghrelin gene peptides in the endocrine pancreas. J Mol Endocrinol 45:107–118 - PubMed
-
- Lim CT, Kola B, Korbonits M, Grossman AB. 2010. Ghrelin's role as a major regulator of appetite and its other functions in neuroendocrinology. Prog Brain Res 182:189–205 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

