Acute and sustained effects of cognitive emotion regulation in major depression
- PMID: 21106812
- PMCID: PMC6633759
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1856-10.2010
Acute and sustained effects of cognitive emotion regulation in major depression
Abstract
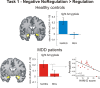
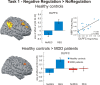
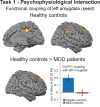
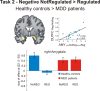
Dysfunctional regulation of mood and emotion is a key component of major depressive disorder and leads to sustained negative feelings. Using functional MRI (fMRI), we investigated the temporal dynamics of emotion regulation in patients with major depressive disorder and in healthy controls, testing for acute and sustained neural effects of active emotion regulation. Moderately depressed individuals (n = 17) and never-depressed healthy control subjects (n = 17) underwent fMRI during performance of an active cognitive emotion regulation task while viewing emotionally arousing pictures. In a second task, completed 15 min later, subjects were presented with the same stimuli in a passive viewing task. Whole-brain analyses and connectivity measures were used to determine acute and sustained effects of emotion regulation on brain activation and coupling between regions. On the group level, patients were able to downregulate negative emotions and corresponding amygdala activation, but this ability decreased with increasing symptom severity. Moreover, only healthy control subjects showed a sustained regulation effect in the amygdala after a 15 min delay, whereas depressed patients did not. Finally, patients exhibited diminished prefrontal activation and reduced prefrontolimbic coupling during active regulation. Although emotion regulation capacity in medicated depressive patients appears to be preserved depending on symptom severity, the effect is not sustained. Correlational analyses provide evidence that this diminished sustained-regulation effect might be related to reduced prefrontal activation during regulation.
Figures
References
-
- Abler B, Erk S, Herwig U, Walter H. Anticipation of aversive stimuli activates extended amygdala in unipolar depression. J Psychiatr Res. 2007;41:511–522. - PubMed
-
- Anand A, Li Y, Wang Y, Wu J, Gao S, Bukhari L, Mathews VP, Kalnin A, Lowe MJ. Antidepressant effect on connectivity of the mood-regulating circuit: an FMRI study. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2005;30:1334–1344. - PubMed
-
- Beauregard M, Paquette V, Lévesque J. Dysfunction in the neural circuitry of emotional self-regulation in major depressive disorder. Neuroreport. 2006;17:843–846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
