ELOVL2 controls the level of n-6 28:5 and 30:5 fatty acids in testis, a prerequisite for male fertility and sperm maturation in mice
- PMID: 21106902
- PMCID: PMC3023544
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M011346
ELOVL2 controls the level of n-6 28:5 and 30:5 fatty acids in testis, a prerequisite for male fertility and sperm maturation in mice
Abstract
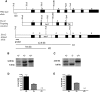
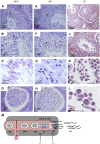
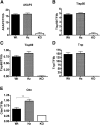
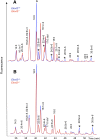
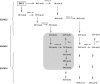
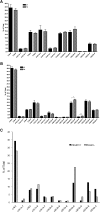
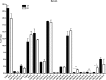
ELOVL2 is a member of the mammalian microsomal ELOVL fatty acid enzyme family, involved in the elongation of very long-chain fatty acids including PUFAs required for various cellular functions in mammals. Here, we used ELOVL2-ablated (Elovl2(-/-)) mice to show that the PUFAs with 24-30 carbon atoms of the ω-6 family in testis are indispensable for normal sperm formation and fertility in male mice. The lack of Elovl2 was associated with a complete arrest of spermatogenesis, with seminiferous tubules displaying only spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes without further germinal cells. Furthermore, based on acyl-CoA profiling, heterozygous Elovl2(+/-) male mice exhibited haploinsufficiency, with reduced levels of C28:5 and C30:5n-6 PUFAs, which gave rise to impaired formation and function of haploid spermatides. These new insights reveal a novel mechanism involving ELOVL2-derived PUFAs in mammals and previously unrecognized roles for C28 and C30 n-6 PUFAs in male fertility. In accordance with the function suggested for ELOVL2, the Elovl2(-/-) mice show distorted levels of serum C20 and C22 PUFAs from both the n-3 and the n-6 series. However, dietary supplementation with C22:6n-3 could not restore male fertility to Elovl2(+/-) mice, suggesting that the changes in n-6 fatty acid composition seen in the testis of the Elovl2(+/-) mice, cannot be compensated by increased C22:6n-3 content.
Figures
References
-
- Burr G. O., Burr M. M. 1973. Nutrition classics from The Journal of Biological Chemistry 82:345–67, 1929. A new deficiency disease produced by the rigid exclusion of fat from the diet. Nutr. Rev. 31: 248–249. - PubMed
-
- Guillou H., Zadravec D., Martin P. G., Jacobsson A. 2010. The key roles of elongases and desaturases in mammalian fatty acid metabolism: Insights from transgenic mice. Prog. Lipid Res. 49: 186–199. - PubMed
-
- Mandal M. N., Ambasudhan R., Wong P. W., Gage P. J., Sieving P. A., Ayyagari R. 2004. Characterization of mouse orthologue of ELOVL4: genomic organization and spatial and temporal expression. Genomics. 83: 626–635. - PubMed
-
- Leonard A. E., Bobik E. G., Dorado J., Kroeger P. E., Chuang L. T., Thurmond J. M., Parker-Barnes J. M., Das T., Huang Y. S., Mukerji P. 2000. Cloning of a human cDNA encoding a novel enzyme involved in the elongation of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochem. J. 350: 765–770. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

