Dietary sodium modulates the interaction between efferent and afferent renal nerve activity by altering activation of α2-adrenoceptors on renal sensory nerves
- PMID: 21106912
- PMCID: PMC3043795
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00469.2010
Dietary sodium modulates the interaction between efferent and afferent renal nerve activity by altering activation of α2-adrenoceptors on renal sensory nerves
Abstract
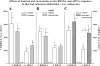
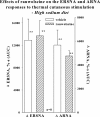
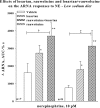
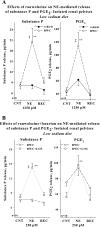
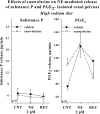
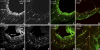
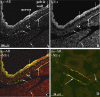
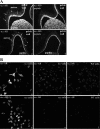
Activation of efferent renal sympathetic nerve activity (ERSNA) increases afferent renal nerve activity (ARNA), which then reflexively decreases ERSNA via activation of the renorenal reflexes to maintain low ERSNA. The ERSNA-ARNA interaction is mediated by norepinephrine (NE) that increases and decreases ARNA by activation of renal α(1)-and α(2)-adrenoceptors (AR), respectively. The ERSNA-induced increases in ARNA are suppressed during a low-sodium (2,470 ± 770% s) and enhanced during a high-sodium diet (5,670 ± 1,260% s). We examined the role of α(2)-AR in modulating the responsiveness of renal sensory nerves during low- and high-sodium diets. Immunohistochemical analysis suggested the presence of α(2A)-AR and α(2C)-AR subtypes on renal sensory nerves. During the low-sodium diet, renal pelvic administration of the α(2)-AR antagonist rauwolscine or the AT1 receptor antagonist losartan alone failed to alter the ARNA responses to reflex increases in ERSNA. Likewise, renal pelvic release of substance P produced by 250 pM NE (from 8.0 ± 1.3 to 8.5 ± 1.6 pg/min) was not affected by rauwolscine or losartan alone. However, rauwolscine+losartan enhanced the ARNA responses to reflex increases in ERSNA (4,680 ± 1,240%·s), and renal pelvic release of substance P by 250 pM NE, from 8.3 ± 0.6 to 14.2 ± 0.8 pg/min. During a high-sodium diet, rauwolscine had no effect on the ARNA response to reflex increases in ERSNA or renal pelvic release of substance P produced by NE. Losartan was not examined because of low endogenous ANG II levels in renal pelvic tissue during a high-sodium diet. Increased activation of α(2)-AR contributes to the reduced interaction between ERSNA and ARNA during low-sodium intake, whereas no/minimal activation of α(2)-AR contributes to the enhanced ERSNA-ARNA interaction under conditions of high sodium intake.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of renal sensory nerves in physiological and pathophysiological conditions.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015 Jan 15;308(2):R79-95. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00351.2014. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25411364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary sodium modulates the interaction between efferent renal sympathetic nerve activity and afferent renal nerve activity: role of endothelin.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):R337-51. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.91029.2008. Epub 2009 May 27. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19474389 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired interaction between efferent and afferent renal nerve activity in SHR involves increased activation of alpha2-adrenoceptors.Hypertension. 2011 Mar;57(3):640-7. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.166595. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Hypertension. 2011. PMID: 21263127
-
Renal sympathetic nerve activity modulates afferent renal nerve activity by PGE2-dependent activation of alpha1- and alpha2-adrenoceptors on renal sensory nerve fibers.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007 Oct;293(4):R1561-72. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00485.2007. Epub 2007 Aug 15. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17699565
-
Endothelin in the control of renal sympathetic nerve activity.Contrib Nephrol. 2011;172:107-119. doi: 10.1159/000328688. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Contrib Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21893993 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal sensory and sympathetic nerves reinnervate the kidney in a similar time-dependent fashion after renal denervation in rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013 Apr 15;304(8):R675-82. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00599.2012. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23408032 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Sympathetic Nervous System and Its Modulation in Renal Hypertension.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018 Mar 29;5:82. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00082. eCollection 2018. Front Med (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29651418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between the nervous system and the kidney.Kidney Int. 2020 Mar;97(3):466-476. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.10.032. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32001065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of renal sensory nerves in physiological and pathophysiological conditions.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015 Jan 15;308(2):R79-95. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00351.2014. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25411364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of α2-Adrenoceptors in Hypertension: Focus on Renal Sympathetic Neurotransmitter Release, Inflammation, and Sodium Homeostasis.Front Physiol. 2020 Nov 9;11:566871. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.566871. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33240096 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bylund DB, Eikenberg DC, Hieble JP, Langer SZ, Lefkowitz RJ, Minneman KP, Molinoff PB, Ruffolo RJ, Trendelenburg U. International Union of Pharmacology nomenclature of adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Rev 46: 121–136, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Cho HJ, Kim DS, Lee NH, Kim JK, Lee KM, Han KS, Kang YN, Kim KJ. Changes in the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtypes gene expression in rat dorsal root ganglion in an experimental model of neuropathic pain. Neuroreport 8: 3119−–3122., 1997 - PubMed
-
- DiBona GF, Jones SY, Sawin LL. Effect of endogenous angiotensin II on renal nerve activity and its arterial baroreflex regulation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 271: R361–R367, 1996 - PubMed
-
- DiBona GF, Kopp UC. Neural control of renal function. Physiol Rev 77: 75–197, 1997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

