Formin homology domain-containing protein 1 regulates smooth muscle cell phenotype
- PMID: 21106951
- PMCID: PMC3025477
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.212993
Formin homology domain-containing protein 1 regulates smooth muscle cell phenotype
Abstract
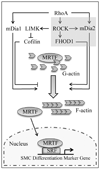
Objective: Our goal was to test whether formin homology protein 1 (FHOD1) plays a significant role in the regulation of smooth muscle cell (SMC) differentiation and, if so, whether Rho kinase (ROCK)-dependent phosphorylation in the diaphanous autoinhibitory domain is an important signaling mechanism that controls FHOD1 activity in SMC.
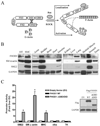
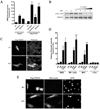
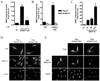
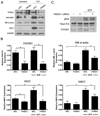
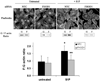
Methods and results: FHOD1 is highly expressed in aortic SMCs and in tissues with a significant SMC component. Exogenous expression of constitutively active FHOD1, but not wild-type, strongly activated SMC-specific gene expression in 10T1/2 cells. Treatment of SMC with the RhoA activator sphingosine-1-phosphate increased FHOD1 phosphorylation at Thr1141, and this effect was completely prevented by inhibition of ROCK with Y-27632. Phosphomimetic mutations to ROCK target residues enhanced FHOD1 activity, suggesting that phosphorylation interferes with FHOD1 autoinhibition. Importantly, knockdown of FHOD1 in SMC strongly inhibited sphingosine-1-phosphate-dependent increases in SMC differentiation marker gene expression and actin polymerization, suggesting that FHOD1 plays a major role in RhoA-dependent signaling in SMC.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that FHOD1 is a critical regulator of SMC phenotype and is regulated by ROCK-dependent phosphorylation. Thus, additional studies on the role of FHOD1 during development and the progression of cardiovascular disease will be important.
Figures
References
-
- Owens GK, Kumar MS, Wamhoff BR. Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in development and disease. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:767–801. - PubMed
-
- Landerholm TE, Dong XR, Lu J, Belaguli NS, Schwartz RJ, Majesky MW. A role for serum response factor in coronary smooth muscle differentiation from proepicardial cells. Development. 1999;126:2053–2062. - PubMed
-
- Niu Z, Yu W, Zhang SX, Barron M, Belaguli NS, Schneider MD, Parmacek M, Nordheim A, Schwartz RJ. Conditional mutagenesis of the murine serum response factor gene blocks cardiogenesis and the transcription of downstream gene targets. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:32531–32538. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

