Fibrinopeptides A and B release in the process of surface fibrin formation
- PMID: 21106983
- PMCID: PMC3056594
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-08-300301
Fibrinopeptides A and B release in the process of surface fibrin formation
Abstract
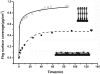
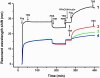
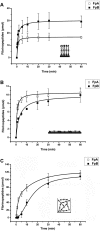
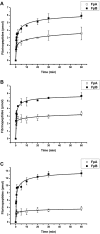
Fibrinogen adsorption on a surface results in the modification of its functional characteristics. Our previous studies revealed that fibrinogen adsorbs onto surfaces essentially in 2 different orientations depending on its concentration in the solution: "side-on" at low concentrations and "end-on" at high concentrations. In the present study, we analyzed the thrombin-mediated release of fibrinopeptides A and B (FpA and FpB) from fibrinogen adsorbed in these orientations, as well as from surface-bound fibrinogen-fibrin complexes prepared by converting fibrinogen adsorbed in either orientation into fibrin and subsequently adding fibrinogen. The release of fibrinopeptides from surface-adsorbed fibrinogen and from surface-bound fibrinogen-fibrin complexes differed significantly compared with that from fibrinogen in solution. The release of FpB occurred without the delay (lag phase) characteristic of its release from fibrinogen in solution. The amount of FpB released from end-on adsorbed fibrinogen and from adsorbed fibrinogen-fibrin complexes was much higher than that of FpA. FpB is known as a potent chemoattractant, so its preferential release suggests a physiological purpose in the attraction of cells to the site of injury. The N-terminal portions of fibrin β chains including residues Bβ15-42, which are exposed after cleavage of FpB, have been implicated in many processes, including angiogenesis and inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Geer CB, Tripathy A, Schoenfisch MH, Lord ST, Gorkun OV. Role of B-b knob-hole interactions in fibrin binding to adsorbed fibrinogen. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5(12):2344–2351. - PubMed
-
- Geer CB, Rus IA, Lord ST, Schoenfisch MH. Surface-dependent fibrinopeptide A accessibility to thrombin. Acta Biomater. 2007;3(5):663–668. - PubMed
-
- Evans-Nguyen KM, Fuierer RR, Fitchett BD, Tolles LR, Conboy JC, Schoenfisch MH. Changes in adsorbed fibrinogen upon conversion to fibrin. Langmuir. 2006;22(11):5115–5121. - PubMed
-
- Soman P, Rice Z, Siedliecki CA. Measuring the time-dependent functional activity of adsorbed fibrinogen by atomic force microscopy. Langmuir. 2008;24(16):8801–8806. - PubMed
-
- Savage B, Ruggeri ZM. Selective recognition of adhesive sites in surface-bound fibrinogen by glycoprotein IIb-IIIa on nonactivated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(17):11227–11233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

