CP-690,550, a therapeutic agent, inhibits cytokine-mediated Jak3 activation and proliferation of T cells from patients with ATL and HAM/TSP
- PMID: 21106989
- PMCID: PMC3056641
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-09-305425
CP-690,550, a therapeutic agent, inhibits cytokine-mediated Jak3 activation and proliferation of T cells from patients with ATL and HAM/TSP
Abstract
The retrovirus, human T-cell-lymphotrophic virus-1 (HTLV-I) is the etiologic agent of adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) and the neurological disorder HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). The HTLV-I-encoded protein tax constitutively activates interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-9, and IL-15 autocrine/paracrine systems that in turn activate the Jak3 (Janus kinase 3)/STAT5 (signal transducers and activators of transcription 5) pathway, suggesting a therapeutic strategy that involves targeting Jak3. We evaluated the action of the Jak3 inhibitor CP-690,550 on cytokine dependent ex vivo proliferation that is characteristic of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from select patients with smoldering or chronic subtypes of ATL, or from those with HAM/TSP whose PBMCs are associated with autocrine/paracrine pathways that involve the production of IL-2, IL-9, IL-15, and their receptors. CP-690,550 at 50 nM inhibited the 6-day ex vivo spontaneous proliferation of PBMCs from ATL and HAM/TSP patients by 67.1% and 86.4%, respectively. Furthermore, CP-690,550 inhibited STAT5 phosphorylation in isolated ATL T cells ex vivo. Finally, in an in vivo test of biological activity, CP-690,550 treatment of mice with a CD8 T-cell IL-15-transgenic leukemia that manifests an autocrine IL-15/IL-15Rα pathway prolonged the survival duration of these tumor-bearing mice. These studies support further evaluation of the Jak3 inhibitor CP-690,550 in the treatment of select patients with HTLV-I-associated ATL and HAM/TSP.
Figures
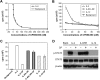


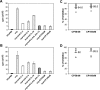


Comment in
-
JAK blockade and HTLV.Blood. 2011 Feb 10;117(6):1771-2. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-12-322008. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21310928 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cytokine induction in HTLV-I associated myelopathy and adult T-cell leukemia: alternate molecular mechanisms underlying retroviral pathogenesis.J Cell Biochem. 1991 Aug;46(4):302-11. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240460405. J Cell Biochem. 1991. PMID: 1757474
-
Selective targeting of JAK/STAT signaling is potentiated by Bcl-xL blockade in IL-2-dependent adult T-cell leukemia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Oct 6;112(40):12480-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1516208112. Epub 2015 Sep 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26396258 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo expression of the HBZ gene of HTLV-1 correlates with proviral load, inflammatory markers and disease severity in HTLV-1 associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP).Retrovirology. 2009 Feb 19;6:19. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-6-19. Retrovirology. 2009. PMID: 19228429 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and cellular immune response in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis.J Neurovirol. 2020 Oct;26(5):652-663. doi: 10.1007/s13365-020-00881-w. Epub 2020 Jul 23. J Neurovirol. 2020. PMID: 32705480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A refractory human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis patient with lymphoma-type adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: A case report and review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Oct 8;100(40):e27450. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027450. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34622865 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
STAT5 inhibition induces TRAIL/DR4 dependent apoptosis in peripheral T-cell lymphoma.Oncotarget. 2018 Mar 30;9(24):16792-16806. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24698. eCollection 2018 Mar 30. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29682185 Free PMC article.
-
Tofacitinib overcomes an IFNγ-induced decrease in NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity via the regulation of immune-related molecules in LC-2/ad.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Mar;12(6):775-782. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13847. Epub 2021 Jan 24. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33491334 Free PMC article.
-
Disorders of the JAK/STAT Pathway in T Cell Lymphoma Pathogenesis: Implications for Immunotherapy.Annu Rev Immunol. 2017 Apr 26;35:533-550. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-110416-120628. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Annu Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28182501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell surface markers in HTLV-1 pathogenesis.Viruses. 2011 Aug;3(8):1439-59. doi: 10.3390/v3081439. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21994790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tofacitinib induces G1 cell-cycle arrest and inhibits tumor growth in Epstein-Barr virus-associated T and natural killer cell lymphoma cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 22;7(47):76793-76805. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12529. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27732937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gessain A, Barin F, Vernant JC, et al. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1985;2(8452):407–410. - PubMed
-
- Osame M, Usuku K, Izumo S, et al. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet. 1986;1(8488):1031–1032. - PubMed
-
- Uchiyama T, Yodoi J, Sagawa K, Takatsuki K, Uchino H. Adult T-cell leukemia: clinical and hematologic features of 16 cases. Blood. 1977;50(3):481–492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

