Liver cytochrome P450 3A endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation: a major role for the p97 AAA ATPase in cytochrome P450 3A extraction into the cytosol
- PMID: 21107009
- PMCID: PMC3030383
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.186981
Liver cytochrome P450 3A endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation: a major role for the p97 AAA ATPase in cytochrome P450 3A extraction into the cytosol
Abstract
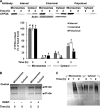
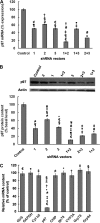
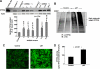
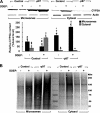
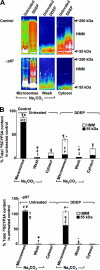
The CYP3A subfamily of hepatic cytochromes P450, being engaged in the metabolism and clearance of >50% of clinically relevant drugs, can significantly influence therapeutics and drug-drug interactions. Our characterization of CYP3A degradation has indicated that CYPs 3A incur ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation (UPD) in an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated degradation (ERAD) process. Cytochromes P450 are monotopic hemoproteins N-terminally anchored to the ER membrane with their protein bulk readily accessible to the cytosolic proteasome. Given this topology, it was unclear whether they would require the AAA-ATPase p97 chaperone complex that retrotranslocates/dislocates ubiquitinated ER-integral and luminal proteins into the cytosol for proteasomal delivery. To assess the in vivo relevance of this p97-CYP3A association, we used lentiviral shRNAs to silence p97 (80% mRNA and 90% protein knockdown relative to controls) in sandwich-cultured rat hepatocytes. This extensive hepatic p97 knockdown remarkably had no effect on cellular morphology, ER stress, and/or apoptosis, despite the well recognized strategic p97 roles in multiple important cellular processes. However, such hepatic p97 knockdown almost completely abrogated CYP3A extraction into the cytosol, resulting in a significant accumulation of parent and ubiquitinated CYP3A species that were firmly ER-tethered. Little detectable CYP3A accumulated in the cytosol, even after concomitant inhibition of proteasomal degradation, thereby documenting a major role of p97 in CYP3A extraction and delivery to the 26 S proteasome during its UPD/ERAD. Intriguingly, the accumulated parent CYP3A was functionally active, indicating that p97 can regulate physiological CYP3A content and thus influence its clinically relevant function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the physiological turnover of native and inactivated cytochromes P450 3A in cultured rat hepatocytes: a role for the cytosolic AAA ATPase p97?Biochemistry. 2007 Jul 3;46(26):7793-803. doi: 10.1021/bi700340n. Epub 2007 Jun 6. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17550236 Free PMC article.
-
Liver cytochrome P450 3A ubiquitination in vivo by gp78/autocrine motility factor receptor and C terminus of Hsp70-interacting protein (CHIP) E3 ubiquitin ligases: physiological and pharmacological relevance.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 12;285(46):35866-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.167189. Epub 2010 Sep 6. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20819951 Free PMC article.
-
The AAA-ATPase p97 facilitates degradation of apolipoprotein B by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.J Lipid Res. 2008 Oct;49(10):2149-60. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800108-JLR200. Epub 2008 Jun 11. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 18550891
-
The final moments of misfolded proteins en route to the proteasome.DNA Cell Biol. 2014 Aug;33(8):477-83. doi: 10.1089/dna.2014.2452. Epub 2014 May 15. DNA Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24833120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of p97/Cdc48p in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation: from the immune system to yeast.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;300:95-125. doi: 10.1007/3-540-28007-3_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16573238 Review.
Cited by
-
Inadequate fine-tuning of protein synthesis and failure of amino acid homeostasis following inhibition of the ATPase VCP/p97.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Dec 31;6(12):e2031. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.373. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26720340 Free PMC article.
-
Multisite phosphorylation of human liver cytochrome P450 3A4 enhances Its gp78- and CHIP-mediated ubiquitination: a pivotal role of its Ser-478 residue in the gp78-catalyzed reaction.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Feb;11(2):M111.010132. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.010132. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22101235 Free PMC article.
-
The p97/VCP ATPase is critical in muscle atrophy and the accelerated degradation of muscle proteins.EMBO J. 2012 Aug 1;31(15):3334-50. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.178. Epub 2012 Jul 6. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22773186 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Ultrastructural and Computational Approaches Reveals the Protective Effect of Astaxanthin against BPA-Induced Nephrotoxicity.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 1;11(2):421. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020421. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830956 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic cytochrome P450 ubiquitination: conformational phosphodegrons for E2/E3 recognition?IUBMB Life. 2014 Feb;66(2):78-88. doi: 10.1002/iub.1247. Epub 2014 Feb 3. IUBMB Life. 2014. PMID: 24488826 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guengerich F. P. (2005) Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism and Biochemistry (Ortiz de Montellano P. ed) pp. 377–530, Kluwer-Academic/Plenum Press, New York
-
- Vergères G., Winterhalter K. H., Richter C. (1989) Biochemistry 28, 3650–3655 - PubMed
-
- Brown C. A., Black S. D. (1989) J. Biol. Chem. 264, 4442–4449 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

