Serum antibody titers against heat shock protein 27 are associated with the severity of coronary artery disease
- PMID: 21107776
- PMCID: PMC3077226
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-010-0241-7
Serum antibody titers against heat shock protein 27 are associated with the severity of coronary artery disease
Abstract
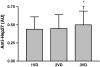
Antibody titers to several heat shock proteins (anti-Hsps) have been reported to be associated with the severity and progression of cardiovascular disease. However, there are little data regarding anti-Hsp27 titers in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). A total of 400 patients with suspected CAD were recruited. Based on the results of coronary angiography, these patients were classified into CAD(+) (n = 300) and CAD(-) (n = 100) groups defined as patients with ≥50% and <50% stenosis of any major coronary artery, respectively. Eighty-three healthy subjects were also recruited as the control group. Serum anti-Hsp27 IgG titers were measured using an in-house enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. CAD(+) patients had significantly higher anti-Hsp27 titers compared with both CAD(-) and control groups. Anti-Hsp27 titers were also higher in the CAD(-) group compared with the control group. With regard to the number of affected vessels in the CAD(+) group, patients with three-vessel disease had higher anti-Hsp27 titers compared with both two-vessel disease (2VD) and one-vessel disease (1VD) subgroups. However, there was no significant difference between 1VD and 2VD subgroups. In multiple linear regression analysis, the number of narrowed vessels and smoking were significant independent determinants of serum anti-Hsp27 titers. The present findings indicate that serum anti-Hsp27 titers may be associated with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A cross-sectional study of the association between heat shock protein 27 antibody titers, pro-oxidant-antioxidant balance and metabolic syndrome in patients with angiographically-defined coronary artery disease.Clin Biochem. 2011 Dec;44(17-18):1390-5. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2011.09.011. Epub 2011 Oct 2. Clin Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21986591
-
Prognostic Factors Associating with Pro-oxidant-antioxidant Balance; Neutrophils to Lymphocytes Ratio, Vitamin D, Heat Shock Protein 27, and Red Cell Distribution Width.Arch Med Res. 2020 Apr;51(3):261-267. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.02.006. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Arch Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32111498
-
Serum immunoglobulin G antibodies to chlamydial heat shock protein 60 but not to human and bacterial homologs are associated with coronary artery disease.Circulation. 2002 Sep 24;106(13):1659-63. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000031567.10814.d8. Circulation. 2002. PMID: 12270859
-
Prevalence of Antinuclear Antibodies in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease: A Scoping Review.Cureus. 2025 Feb 12;17(2):e78915. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78915. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40091923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the role of exercise in modulating plasma heat shock protein 27 levels: insights for exercise immunology and cardiovascular health.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Mar;480(3):1381-1401. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05089-8. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39172352 Review.
Cited by
-
GCAP1, Rab6, and HSP27: Novel Autoantibody Targets in Cancer-Associated Retinopathy and Autoimmune Retinopathy.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2016 May 2;5(3):1. doi: 10.1167/tvst.5.3.1. eCollection 2016 May. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 27152249 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in anti-heat shock protein 27 antibody and C-reactive protein levels following cardiac surgery and their association with cardiac function in patients with cardiovascular disease.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013 Jan;18(1):65-74. doi: 10.1007/s12192-012-0358-y. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013. PMID: 22843452 Free PMC article.
-
Coronary artery disease and its risk factors status in iran: a review.Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2011 Sep;13(9):610-23. doi: 10.5812/kowsar.20741804.2286. Epub 2011 Sep 15. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2011. PMID: 24069531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased expression of phosphorylated forms of heat-shock protein-27 and p38MAPK in macrophage-rich regions of fibro-fatty atherosclerotic lesions in the rabbit.Int J Exp Pathol. 2016 Feb;97(1):56-65. doi: 10.1111/iep.12167. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Int J Exp Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26853073 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into heat shock protein 27, a potential therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 May 12;10:1195464. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1195464. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37252119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bluhm WF, Martin JL, Mestril R, Dillmann WH. Specific heat shock proteins protect microtubules during simulated ischemia in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:H2243–H2249. - PubMed
-
- Burian K, Kis Z, Virok D, Endresz V, Prohaszka Z, Duba J, Berencsi K, Boda K, Horvath L, Romics L, Fust G, Gonczol E. Independent and joint effects of antibodies to human heat-shock protein 60 and Chlamydia pneumoniae infection in the development of coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2001;103:1503–1508. - PubMed
-
- Corrado E, Rizzo M, Coppola G, Fattouch K, Novo G, Marturana I, Ferrara F, Novo S. An update on the role of markers of inflammation in atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2010;17:1–11. - PubMed
-
- De AK, Kodys KM, Yeh BS, Miller-Graziano C. Exaggerated human monocyte IL-10 concomitant to minimal TNF-alpha induction by heat-shock protein 27 (Hsp27) suggests Hsp27 is primarily an anti-inflammatory stimulus. J Immunol. 2000;165:3951–3958. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

