Rapamycin increases the yield and effector function of human γδ T cells stimulated in vitro
- PMID: 21107834
- PMCID: PMC3077899
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-010-0945-7
Rapamycin increases the yield and effector function of human γδ T cells stimulated in vitro
Abstract
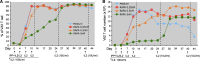
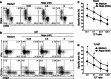
Clinical strategies to exploit Vγ2Vδ2 T cell responses for immunotherapy are confronted with short-term increases in cell levels or activity and the development of anergy that reduces the response to therapy with succeeding treatments. We are exploring strategies to increase the yield and durability of elicited Vγ2Vδ2 T cell responses. One approach focuses on the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), which is important for regulating T cell metabolism and function. In Vγ2Vδ2 T cells, mTOR phosphorylates the S6K1 and eIF4EBP1 signaling intermediates after antigen stimulation. Rapamycin inhibited these phosphorylation events without impacting Akt or Erk activation, even though specific inhibition of Akt or Erk in turn reduced the activation of mTOR. The effects of rapamycin on the T cell receptor signaling pathway lead to increased proliferation of treated and antigen-exposed Vγ2Vδ2 cells. Rapamycin altered the phenotype of antigen-specific Vγ2Vδ2 cells by inducing a population shift from CD62L + CD69- to CD62L-CD69+, higher expression of CD25 or Bcl-2, lower levels of CCR5 and increased resistance to Fas-mediated cellular apoptosis. These changes were consistent with rapamycin promoting cell activation while decreasing the susceptibility to cell death that might occur by CCR5 or Fas signaling. Rapamycin treatment during antigen-stimulation of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells may be a strategy for overcoming current obstacles in tumor immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Different patterns of Akt and ERK feedback activation in response to rapamycin, active-site mTOR inhibitors and metformin in pancreatic cancer cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057289. Epub 2013 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437362 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin interacts synergistically with idarubicin to induce T-leukemia cell apoptosis in vitro and in a mesenchymal stem cell simulated drug-resistant microenvironment via Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin and extracellular signal-related kinase signaling pathways.Leuk Lymphoma. 2014 Mar;55(3):668-76. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.811579. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014. PMID: 23741975
-
Protein phosphatase 2A and DNA-dependent protein kinase are involved in mediating rapamycin-induced Akt phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 10;288(19):13215-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.463679. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23536185 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin: a central node of complex signaling cascades.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011 Jun 20;4(5):476-95. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21738819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A critical role for non-coding RNA GAS5 in growth arrest and rapamycin inhibition in human T-lymphocytes.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Apr;39(2):482-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0390482. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21428924 Review.
Cited by
-
HDAC Inhibitor LBH589 Suppresses the Proliferation but Enhances the Antileukemic Effect of Human γδT Cells.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020 Aug 8;18:623-630. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.08.003. eCollection 2020 Sep 25. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020. PMID: 33005729 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of γδ T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:2932531. doi: 10.1155/2016/2932531. Epub 2016 Feb 11. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 26981547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-viral and Apoptotic Induction of m-TOR Inhibitor Drugs against Hepatitis C Virus Activity and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line: In vitro and in silico.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Oct 1;25(10):3725-3739. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.10.3725. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39471041 Free PMC article.
-
Bordeaux 2018: Wine, Cheese, and γδ T Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 25;10:2544. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02544. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31708934 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Enhancing adoptive cancer immunotherapy with Vγ2Vδ2 T cells through pulse zoledronate stimulation.J Immunother Cancer. 2017 Feb 21;5:9. doi: 10.1186/s40425-017-0209-6. eCollection 2017. J Immunother Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28239463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander AA, Maniar A, Cummings JS, Hebbeler AM, Schulze DH, Gastman BR, Pauza CD, Strome SE, Chapoval AI. Isopentenyl pyrophosphate-activated cd56 + gamma}{delta T lymphocytes display potent antitumor activity toward human squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(13):4232–4240. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4912. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Qin G, Mao H, Zheng J, Sia SF, Liu Y, Chan PL, Lam KT, Peiris JS, Lau YL, Tu W. Phosphoantigen-expanded human gammadelta T cells display potent cytotoxicity against monocyte-derived macrophages infected with human and avian influenza viruses. J Infect Dis. 2009;200(6):858–865. doi: 10.1086/605413. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

